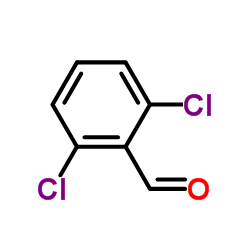
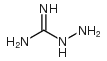
5051-62-7
| Name | 2-[(E)-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylideneamino]guanidine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Guanabenzo
Wy 8678 1-(2,6-Dichlorobenzylideneamino)guanidine WY-8678 Guanabenz monoacetate Wytensin Guanabenzum Wy 8678 base guanabenz |
| Description | Guanabenz is an orally active α-2-adrenoceptor agonist, has antihypertensive effect and antiparasitic activity. Guanabenz interferes ER stress-signalling and has protective effects in cardiac myocytes. Guanabenz also is used for the research of high blood pressure[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Guanabenz (0.5–50 μM, 24 h) is treated with increasing concentrations for 24 hours not affect cell viability. Guanabenz (0.5–50 μM, 24 h) alone not affects the UPR targets, neither on mRNA or protein level nor the phosphorylation status of eIF2a. Guanabenz also not induces GADD34 or the constitutively active form CReP. Guanabenz (0.5–50 μM, 24 h) alone not induces ER stress in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: Neonatal rat cardiac myocytes (NRCM) Concentration: 0.5–50 μM Incubation Time: 24 h Result: Did not affect cell survival. RT-PCR[1] Cell Line: Neonatal rat cardiac myocytes (NRCM) Concentration: 0.5–50 μM Incubation Time: 24 h Result: Did not affect levels of UPR targets. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Neonatal rat cardiac myocytes (NRCM) Concentration: 0.5–50 μM Incubation Time: 24 h Result: Increased the levels of low panel concentration-dependent UPR targets proteins. |
| In Vivo | Guanabenz (5 mg/kg/day; i.p.; for 3 weeks) can reproducibly reduce brain cyst burden. Guanabenz (5 mg /kg/d, i.p., oral; 10 mg/kg/d, gavage; for 3 weeks) reverses Toxoplasma-induced hyperactivity in latently infected mice. Guanabenz (100 and 320 μg/kg and 1 mg/kg, i.v., over a period of 5 min at intervals of 40 min) reduces sympathetic outflow, heart rate and blood pressure in debuffered cats[2][3]. Animal Model: BALB/cJ mice[2] Dosage: 5 mg/kg Administration: 5 mg/kg/day; i.p. ; for 3 weeks Result: Reduced the latent brain cysts in both male and female BALB/cJ mice. Animal Model: BALB/cJ mice[2] Dosage: 5 mg/kg; 10 mg/kg Administration: 5 mg /kg/d, i.p., oral; 10 mg/kg/d, gavage; for 3 weeks Result: Reversed parasite-induced hyperactivity to near-baseline levels. Animal Model: Cats[3] Dosage: 100 and 320 μg/kg and 1 mg/kg Administration: 100 and 320 μg/kg and 1 mg/kg, i.v., over a period of 5 min at intervals of 40 min Result: Declined markedly blood pressure and nerve activity. |
| References |
| Density | 1.49g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 405.7ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 227-229ºC (decomposition) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8Cl2N4 |
| Molecular Weight | 231.08200 |
| Flash Point | 199.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 230.01300 |
| PSA | 74.26000 |
| LogP | 3.00130 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.645 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22-62 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 3249 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2928000090 |
|
~% 
5051-62-7 |
| Literature: Shell Patent: FR1455835 , 1966 ; Chem.Abstr., 1967 , vol. 67, # 11327 |
| HS Code | 2928000090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2928000090 other organic derivatives of hydrazine or of hydroxylamine VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:20.0% |