207556-07-8
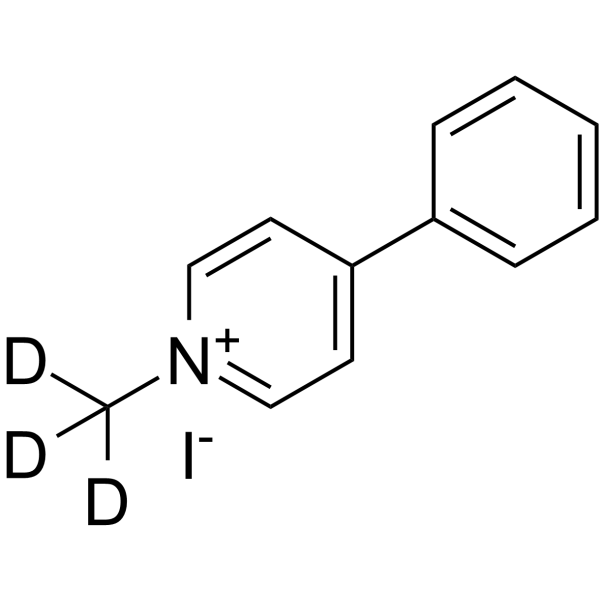
| Name | 4-phenyl-1-(trideuteriomethyl)pyridin-1-ium,iodide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N-Methyl-d3-4-phenylpyridinium iodide
MPP+-d3 Iodide MFCD00134220 |
| Description | MPP+-d3(iodide) is deuterium labeled MPP+ (iodide). MPP+ iodide, a toxic metabolite of the neurotoxin MPTP, causes symptom of Parkinson's disease in animal models by selectively destroying dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. MPP+ iodide is taken up by the dopamine transporter into dopaminergic neurons where it exerts its neurotoxic action on mitochondria by affecting complex I of the respiratory chain. MPP+ iodide is also a high affinity substrate for the serotonin transporter (SERT)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 168-169ºC(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H9D3IN |
| Molecular Weight | 300.15 |
| Exact Mass | 300.02000 |
| PSA | 3.88000 |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311 + H331-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P311 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |