56092-82-1
| Name | Ionomycin calcium salt from Streptomyces conglobatus |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ionomycin calcium salt
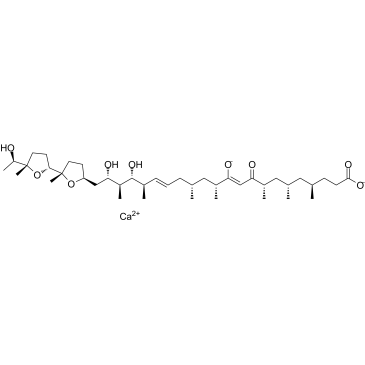
10,16-Docosadienoic acid, 11,19,21-trihydroxy-4,6,8,12,14,18,20-heptamethyl-22-[(2S,2'R,5S,5'S)-octahydro-5'-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2,5'-dimethyl[2,2'-bifuran]-5-yl]-9-oxo-, calcium salt, (4R,6S,8S,10Z,12R,14R,16E,18R,19R,20S,21S)- (1:1) MFCD00151183 Calcium (4R,6S,8S,10Z,12R,14R,16E,18R,19R,20S,21S)-19,21-dihydroxy-22-{(2S,2'R,5S,5'S)-5'-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2,5'-dimethyloctahydro-2,2'-bifuran-5-yl}-4,6,8,12,14,18,20-heptamethyl-11-oxido-9-oxo-10,16-docosadienoate |
| Description | Ionomycin (calcium) is a Calcium ionophore and an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces conglobatus. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Calcium channel[1]. |
| In Vitro | Ionomycin is a Calcium ionophore and an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces conglobatus[1]. Addition of 2 μM Ionomycin to LCLC 103H cells causes an instantaneous increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration from 50 to 180 nM. DNA and protein analysis in Ionomycin-treated cultures revealed DNA fragmentation and PARP cleavage to an 85-kDa fragment typical of caspase-mediated apoptosis. Necrosis could be detected in ~1-5% of the Ionomycin treated cells as supported by simultaneously positive fluorescein labeling and propidium iodide uptake. Caspase activation in whole cells was followed by monitoring the increase in activity against Ac-DEVD-amc following Ionomycin treatment[2]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 817.2ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 205-206ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C41H70CaO9 |
| Molecular Weight | 747.067 |
| Flash Point | 235.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 746.464600 |
| PSA | 131.75000 |
| LogP | 7.64540 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|