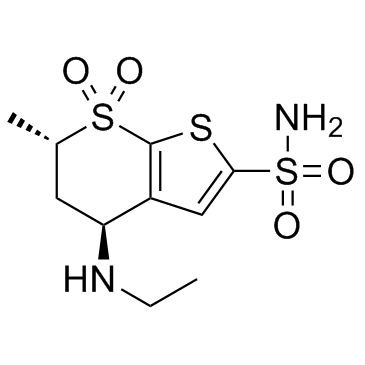
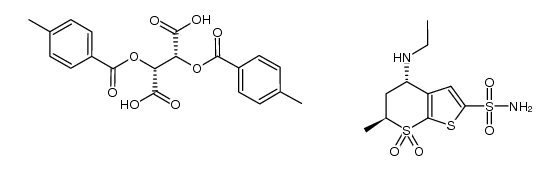
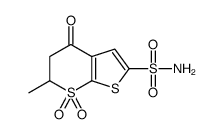
130693-82-2
| Name | dorzolamide hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(4S,6S)-4-(ethylamino)-6-methyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide 7,7-dioxide hydrochloride
4H-Thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide, 4-(ethylamino)-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-, 7,7-dioxide, (4S,6S)-, hydrochloride (1:1) Dorzolamide hydrochloride (4S,6S)-4-(Ethylamino)-6-methyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide 7,7-dioxide hydrochloride (1:1) Dorzolamide HCl Dorzolamide (4S,6S)-4-(Ethylamino)-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-4H-thieno(2,3-b)thiopyran-2-sulfonamide 7,7-dioxide, monohydrochloride (4S,6S)-4-(Ethylamino)-6-methyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamid-7,7-dioxidhydrochlorid 4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide, 4-(ethylamino)-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-, 7,7-dioxide, (4S,6S)-, monohydrochloride (4S,6S)-4-(éthylamino)-6-méthyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-thiéno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide-7,7-dioxyde chlorhydrate MFCD00884659 |
| Description | Dorzolamide Hcl(L671152 Hcl; MK507 Hcl) is an anti-glaucoma agent, which is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.Target: carbonic anhydrase (CA)Dorzolamide hydrochloride is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. It is an anti-glaucoma agent, and acts by decreasing the production of aqueous humour [1]. Glaucoma was induced in the right eye of adult Wistar rats by episcleral venous occlusion. One experimental group was administered dorzolamide hydrochloride 2%-timolol 0.5% combination eye drops, while the other experimental group was administered dorzolamide hydrochloride2% eye drops. Control groups had surgery without drug administration. Drug application was initiated either 2 weeks before surgery (Group A), from the day of surgery (Group B), 2 weeks after surgery (Group C), or 4 weeks after surgery (Group D). RGCs were labeled by intratectal Fluorogold injections and counted from flat-mount preparations, and IOP was measured using Tonopen. Both dorzolamide-timolol combination and dorzolamide hydrochloride, when applied topically, significantly reduced IOP and improved RGC densities in experimental eyes when compared to control eyes. Earlier initiation, as well as longer duration of drug application, resulted in higher RGC densities [2].Clinical indications: Glaucoma; Ocular hypertensionFDA Approved Date: 1995Toxicity: Dizziness, headache, shortness of breath, slow heartbeat, severe asthma, cardiac arrest |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.53 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 575.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 283-285ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H17ClN2O4S3 |
| Molecular Weight | 360.90100 |
| Flash Point | 302ºC |
| Exact Mass | 360.00400 |
| PSA | 151.33000 |
| LogP | 4.66680 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.93E-13mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|
~97% 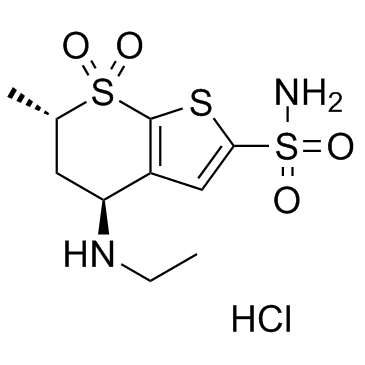
130693-82-2 |
| Literature: RAGACTIVES, S.L. Patent: US2003/220509 A1, 2003 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 12 ; |
|
~99% 
130693-82-2 |
| Literature: CIPLA LIMITED; CURTIS, Philip, Anthony Patent: WO2008/135770 A2, 2008 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 21-22 ; |
|
~% 
130693-82-2 |
| Literature: WO2011/101704 A1, ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2935009090 other sulphonamides VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:35.0% |