42950-74-3
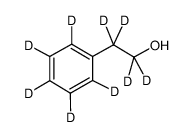
| Name | 2-phenyl-d5-ethan-1,1,2,2-d4-ol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1,1,2,2-tetradeuterio-1,2-diaminoethane
Ethylene-d4-diamine 1,1,2,2-tetradeuterio-2-pentadeuteriophenyl-ethanol Ethylenediamine-C-d4 phenylethanol-d9 tetradeuteroethylenediamine <1,1,2,2-D4>-N,N'-Di-tert-butyl-1,2-ethandiamin |
| Description | 2-Phenylethanol-d9 is the deuterium labeled 2-Phenylethanol[1]. 2-Phenylethanol (Phenethyl alcohol), extracted from rose, carnation, hyacinth, Aleppo pine, orange blossom and other organisms, is a colourless liquid. It has a pleasant floral odor and also an autoantibiotic produced by the fungus Candida albicans[2]. It is used as an additive in cigarettes and also used as a preservative in soaps due to its stability in basic conditions. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C8HD9O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 131.22000 |
| Exact Mass | 131.13000 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 1.22140 |
|
~% 
42950-74-3 |
| Literature: Werstiuk, Nick Henry; Timmins, George Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 1986 , vol. 64, p. 1072 - 1076 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |