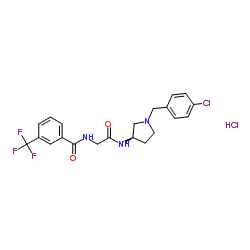
1313730-14-1
| Name | N-(2-{[(3R)-1-(4-Chlorobenzyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]amino}-2-oxoethyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide hydrochloride (1:1) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Benzamide, N-[2-[[(3R)-1-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-3-pyrrolidinyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)-, hydrochloride (1:1)
N-(2-{[(3R)-1-(4-Chlorobenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]amino}-2-oxoethyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide hydrochloride (1:1) N-(2-{[(3R)-1-(4-Chlorobenzyl)-3-pyrrolidinyl]amino}-2-oxoethyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Description | CCR2 antagonist 4 hydrochloride (Teijin compound 1 hydrochloride) is a potent and specific CCR2 antagonist, with IC50s of 180 nM for CCR2b. CCR2 antagonist 4 hydrochloride potently inhibits MCP-1-induced chemotaxis with an IC50 of 24 nM[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CCR2b:180 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Ile263 and Thr292 in CCR2 contribute significantly to binding of CCR2 antagonist 4 in CCR2. Residue Glu291 in TM7, a highly conserved residue in many CC chemokine receptors, contributes substantially to binding of the protonated CCR2 antagonist 4 hydrochloride, and CCL2. His121 on TM3 and Ile263 on TM6 also strongly interact with CCR2 antagonist 4 hydrochloride[2]. |
| In Vivo | In ApoE-deficient mice, Vp-TSL targets specifically aortic plaque endothelial VCAM-1 and CCR2 antagonist 4 hydrochloride reduces the mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7) adhesion/ infiltration into the aorta[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C21H22Cl2F3N3O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 476.319 |
| Exact Mass | 475.104126 |