1227162-34-6
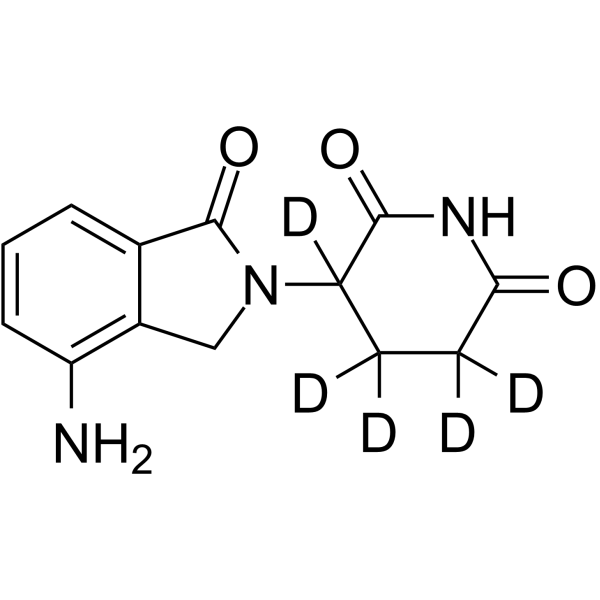
| Name | 3-(4-Amino-1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl)-2,6-(3,4,4,5,5-2H5)piperidinedione |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2,6-Piperidinedione-3,3,4,4,5-d5, 5-(4-amino-1,3-dihydro-1-oxo-2H-isoindol-2-yl)-
MFCD15071270 3-(4-Amino-1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl)-2,6-(3,4,4,5,5-2H5)piperidinedione |
| Description | Lenalidomide-d5 is deuterium labeled Lenalidomide. Lenalidomide (CC-5013), a derivative of Thalidomide, acts as molecular glue. Lenalidomide is an orally active immunomodulator. Lenalidomide (CC-5013) is a ligand of ubiquitin E3 ligase cereblon (CRBN), and it causes selective ubiquitination and degradation of two lymphoid transcription factors, IKZF1 and IKZF3, by the CRBN-CRL4 ubiquitin ligase. Lenalidomide (CC-5013) specifically inhibits growth of mature B-cell lymphomas, including multiple myeloma, and induces IL-2 release from T cells[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 614.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C13H8D5N3O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 264.29 |
| Flash Point | 325.1±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 264.127075 |
| LogP | -1.39 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.672 |