1131342-85-2
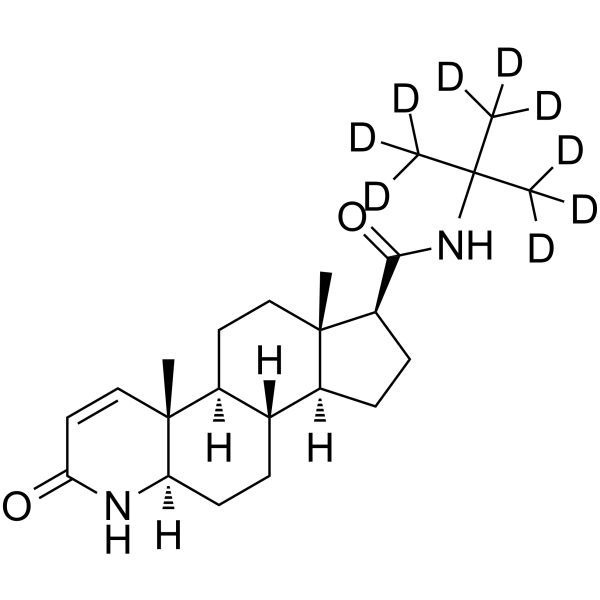
| Name | (4aR,4bS,6aS,7S,9aS,9bS,11aR)-4a,6a-Dimethyl-N-[2-(2H3)methyl(2H6)-2-propanyl]-2-oxo-2,4a,4b,5,6,6a,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-indeno[5,4-f]quinoline-7-carboxamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(4aR,4bS,6aS,7S,9aS,9bS,11aR)-4a,6a-Dimethyl-N-[2-(2H3)methyl(2H6)-2-propanyl]-2-oxo-2,4a,4b,5,6,6a,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-indeno[5,4-f]quinoline-7-carboxamide
MFCD07369399 1H-Indeno[5,4-f]quinoline-7-carboxamide, N-[1,1-di(methyl-d3)ethyl-2,2,2-d3]-2,4a,4b,5,6,6a,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-4a,6a-dimethyl-2-oxo-, (4aR,4bS,6aS,7S,9aS,9bS,11aR)- |
| Description | Finasteride-d9 is deuterium labeled Finasteride. Finasteride (MK-906) is a potent and competitive 5α-reductase inhibitor, with an IC50 of 4.2 nM for type II 5α-reductase. Finasteride has approximately a 100-fold greater affinity for type II 5α-reductase enzyme than for the type I enzyme. Finasteride can be used for the research of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and androgenic alopecia[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
[2]. Flores E, et, al. Steroid 5alpha-reductase inhibitors. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003 May;3(3):225-37. |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 576.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C23H27D9N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 381.60 |
| Flash Point | 177.4±30.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 381.334167 |
| LogP | 3.24 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.524 |