1304701-57-2
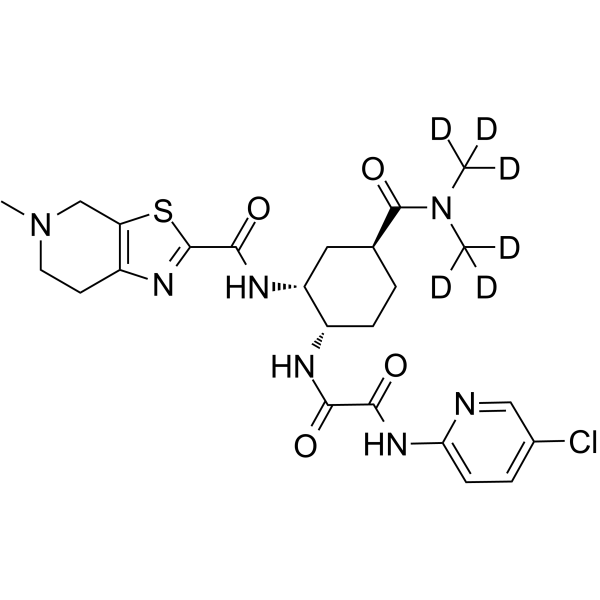
| Name | N-[(1S,2R,4S)-4-{Bis[(2H3)methyl]carbamoyl}-2-{[(5-methyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro[1,3]thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-2-yl)carbonyl]amino}cyclohexyl]-N'-(5-chloro-2-pyridinyl)ethanediamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ethanediamide, N1-(5-chloro-2-pyridinyl)-N2-[(1S,2R,4S)-4-[(dimethyl-d3-amino)carbonyl]-2-[[(4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-5-methylthiazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-2-yl)carbonyl]amino]cyclohexyl]-
N-[(1S,2R,4S)-4-{Bis[(2H3)methyl]carbamoyl}-2-{[(5-methyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro[1,3]thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-2-yl)carbonyl]amino}cyclohexyl]-N'-(5-chloro-2-pyridinyl)ethanediamide |
| Description | Edoxaban-d6 is deuterium labeled Edoxaban. Edoxaban (DU-176) is a selective, potent and orally active factor Xa (FXa) inhibitor with Kis of 0.561 nM and 2.98 nM for free FXa and prothrombinase, respectively. Edoxaban is an anticoagulant agent and can be used for stroke prevention. Edoxaban is a also weak inhibitor of thrombin and factor IXaβ (FIXa), with Kis of 6.00 μM and 41.7 μM, respectively, exhibits >10 000-fold selectivity for FXa. Edoxaban has antithrombotic properties and has potential for thromboembolic diseases treatment[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H24D6ClN7O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 554.09 |
| Exact Mass | 553.214539 |
| LogP | 1.24 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.646 |