57-66-9
| Name | probenecid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Proben
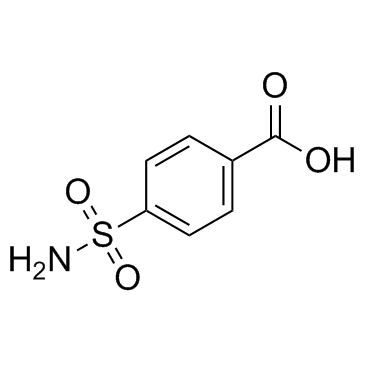
benacen Benuryl EINECS 200-344-3 4-[(di-n-propylamino)sulphonyl]benzoic Acid 4-(Dipropylsulfamoyl)benzoic acid Apurina MFCD00038402 probalan Probecid 4-dipropylsulfamoyl-benzoic acid Probexin probenid 4-(N,N-dipropylaminosulphonyl)benzoic acid benemide Benzoic acid, 4-[(dipropylamino)sulfonyl]- Benemid Probenecid |
| Description | Probenecid is a potent and selective agonist of transient receptor potential vanilloid 2 (TRPV2) channels. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
TRPV2[1] |
| In Vitro | Probenecid efficiently inhibits ATP-dependent active vesicular N-ethylmaleimide glutathione (NEM-GS) uptake by both MRP1 and MRP2. A significant inhibition of the MRP1-ATPase is observed at higher organic anion concentrations. In contrast, the ATPase activity of MRP2 is strongly stimulated by both Probenecid (approximate KACT=250 μM), sulfinpyrazone (KACT=300 μM), and indomethacin (KACT=150 μM), and ATPase activation is even stronger than in the case of NEM-GS. The organic anion activation of the MRP2-ATPase followed bell-shaped curves, with maximum values obtained at about 2 mM for Probenecid, 800 μM for sulfinpyrazone, and 400 μM for indomethacin[2]. Probenecid is an inhibitor of the hTAS2R16, hTAS2R38, and hTAS2R43 bitter taste receptors. Probenecid acts on a subset of TAS2Rs and inhibits through a novel, allosteric mechanism of action. Probenecid is also commonly used to enhance cellular signals in GPCR calcium mobilization assays. Probenecid specifically inhibits the cellular response mediated by the bitter taste receptor hTAS2R16 and provide molecular and pharmacological evidence for direct interaction with this GPCR using a non-competitive (allosteric) mechanism[3]. |
| In Vivo | Administration of Probenecid to WT mice results in increased contractility as measured via ejection fraction (EF) relative to EF in control mice given saline. The increased contractility is noted within 5 minutes of the bolus injection with all doses at or above 75 mg/kg (peak change of 5.26±3.35, 8.40±2.80, 7.32±2.52 for 75mg/kg, 100mg/kg and 200mg/kg, respectively). The measured change in contractility as measured at 5 minute intervals (for 30 minutes total) revealed a dose dependent increase in contractility with an estimated EC50 of 49.33 mg/kg. The EF remained at an elevated state for at least 1 hour on subjects (n=5, dose of 200 mg/kg IV) that are evaluated for a longer period of time (average increase in EF over baseline of 8.9±2.57)[1]. |
| Cell Assay | HEK-293T cells are transfected with hTAS2R expression constructs using Lipofectamine 2000 in poly-lysine coated, black 384-well plates with clear bottoms and incubated for 22 hours at 37°C. Growth media is removed and cells are washed twice with HBSS containing 20 mM HEPES, then loaded with a calcium indicator dye in HBSS containing 20 mM HEPES (Calcium 4 Assay kit) with or without 1 mM Probenecid. Cells are incubated at 37°C for 1 hour in the presence of both dye and Probenecid, then moved to a Flexstation II-384 set for 32°C. After a 15-minute temperature equilibration (without washout), indicated compounds are injected (at t=~25 seconds) and fluorescence is measured for 100 to 180 seconds, reading every 3 seconds. Data sets are analyzed and represented as % over baseline signal using Prism 5.0 software. For Schild plots, replicates of raw calcium flux values are expressed as % over baseline signal. The mean value at 36 seconds (corresponding to the maximum flux signal) for each concentration of TAS2R ligand in the presence of the indicated concentration of Probenecid is plotted against the log of ligand concentration. Data points are fit using non-linear regression in GraphPad Prism[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] In order to obtain a dose response curve, male C57 WT (n=39) mice 12-16 weeks of age are anesthetized with isoflurane while intravenous jugular access (IV) is obtained under a microscope. Subsequently, an echocardiographic study with both M-mode and B-mode is obtained in parasternal long axis (PSLAX) as described below. Either saline or different doses of Probenecid (increasing from 2 to 200mg/kg) are injected (bolus IV) for the initial contractility studies in WT mice. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 438.0±47.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 194-196°C |
| Molecular Formula | C13H19NO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 285.359 |
| Flash Point | 218.7±29.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 285.103485 |
| PSA | 83.06000 |
| LogP | 3.30 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.542 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Stability | Stable, but may be light sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 20 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R40 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37 |
| RIDADR | 3249 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DG9400000 |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2935009090 other sulphonamides VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:35.0% |



![4-[(DIPROPYLAMINO)SULFONYL]BENZENE-1-CARBONYL CHLORIDE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/091/29171-72-0.png)