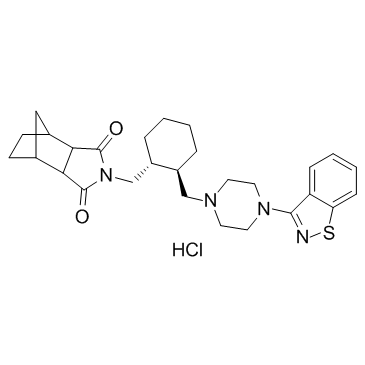
367514-88-3
| Name | lurasidone hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
lurasidone monohydrochloride
Lurasidone Hydrochloride Lurasidone HCl 4,7-Methano-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, 2-[[(1R,2R)-2-[[4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]methyl]cyclohexyl]methyl]hexahydro-, (3aR,4S,7R,7aS)-, hydrochloride (1:1) Lurasidone (Hydrochloride) (1R,2S,6R,7S)-4-{[(1R,2R)-2-{[4-(1,2-Benzothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]methyl}cyclohexyl]methyl}-4-azatricyclo[5.2.1.0]decane-3,5-dione hydrochloride (1:1) Latuda lurasidonhydrochloride |
| Description | Lurasidone is an antagonist of both dopamine D2 and 5-HT7 with IC50s of 1.68 and 0.495 nM, respectively. Lurasidone is also a partial agonist of 5-HT1A receptor with an IC50 of 6.75 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 1.68 nM (dopamine D2), 0.495 nM (5-HT7), 6.75 nM (5-HT1A)[1] |
| In Vitro | Lurasidone is an antagonist of dopamine D2 and 5-HT7 with IC50s of 1.68±0.09 and 0.495±0.090 nM, respectively. Lurasidone is also a partial agonist of 5-HT1A receptor with an IC50 of 6.75±0.97 nM. In vitro receptor binding experiments reveal that Lurasidone demonstrates affinity for dopamine D2 and 5-HT2A receptors higher than other tested antipsychotics. Lurasidone does not increase [35S]GTPγS binding to the membrane preparations for dopamine D2 receptors by itself, but it antagonizes dopamine-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in a concentration-dependent manner with a KB value of 2.8±1.1 nM[1]. |
| In Vivo | Lurasidone dose-dependently increases the ratio of DOPAC/dopamine in both regions, but it shows a preferential effect on the frontal cortex compare with the striatum, especially at higher doses. Lurasidone (ED50 values 2.3 to 5.0 mg/kg) shows a comparable potency with olanzapine (ED50 values 1.1 to 5.1 mg/kg), higher potency than clozapine (ED50 9.5 to 290 mg/kg), and slightly lower potency than haloperidol (ED50 values 0.44 to 1.7 mg/kg). Lurasidone (1 to 10 mg/kg) dose-dependently inhibits conditioned avoidance response (CAR) in rats, and the ED50 values are 6.3 mg/kg. Lurasidone dose-dependently inhibits TRY-induced forepaw clonic seizure and p-CAMP-induced hyperthermia with ED50 values of 5.6 and 3.0 mg/kg, respectively. Lurasidone (0.3 to 30 mg/kg) dose-dependently and significantly increases the number of shocks received by rats in the conflict test with MED of 10 mg/kg (p<0.01)[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | [35S]GTPγS binding experiments for the human dopamine D2L or 5-HT1A receptors stably expressed in the membranes of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are performed. Shortly after dopamine (or serotonin) and/or Lurasidone are incubated for 20 min at room temperature with the cell membrane preparation containing [35S]GTPγS (0.05 nM for D2L or 0.2 nM for 5-HT1A), the membranes are filtered through glass filters and the radioactivity bound to each filter is measured with a liquid scintillation counter[1]. |
| Animal Admin | SD rats are individually isolated in clear plastic cages and injected with methamphetamine (MAP) (1 mg/kg i.p.) 1 h after the administration of drugs or vehicle. In the test of persistence of the effect, Lurasidone is administered 1, 2, 4, and 8 h before the MAP injection. Locomotor activity is measured for 80 min from 10 min after MAP injection. Four or five groups of 6 to 13 rats are used to calculate the ED50 value that inhibits MAP-induced hyperactivity by 50% of the animals tested[1]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 198-205°C |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H37ClN4O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 529.14 |
| Flash Point | 9℃ |
| PSA | 84.99000 |
| LogP | 4.19660 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H301 + H311 + H331-H370 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P260-P280-P301 + P310-P311 |
| Hazard Codes | F,T |
| Risk Phrases | 11-23/24/25-39/23/24/25 |
| Safety Phrases | 7-16-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN1230 - class 3 - PG 2 - Methanol, solution |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |