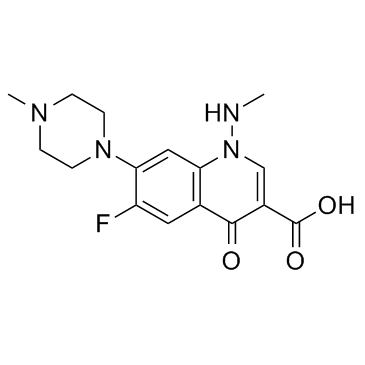
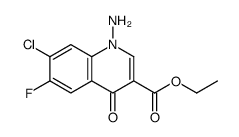
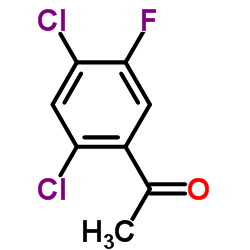
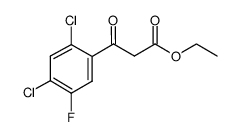
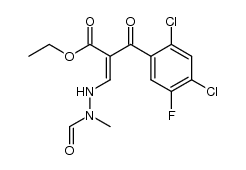
86393-37-5
| Name | amifloxacin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
6-fluoro-1-methylamino-7-(4-methyl-piperazino)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid
6-Fluoro-1,4-dihydro-1-(methylamino)-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid AMFX 1-methylamino-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 1-methylamino-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid 6-Fluoro-1,4-dihydro-1-(methylamino)-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid Win49375 |
| Description | Win49375 is a synthetic antibacterial agent of the quinolone class. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Antibacterial[1] |
| In Vitro | Win49375 (WIN 49375) is active in vitro against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates and shows moderate activity against Staphylococcus aureus, with MICs of less than or equal to 2 μg/mL. |
| In Vivo | WIN 49375 is highly active by the oral route, with 50% effective doses within two- to threefold of those obtained with parenteral medication. The effectiveness of WIN 49375 with various routes of medication is demonstrated with these experimental infections. When mice infected intraperitoneally with E. coli Vogel are medicated at 0.5-h postinfection subcutaneously, intravenously, or orally the ED50s for WIN 49375 are 0.6, 0.8, and 1.0 mg/kg, respectively[1]. Blood radioactivity peaks at 0.5 h after oral administration of [14C]Amifloxacin mesylate to rats at 20 mg/kg and is equivalent to 7.1±0.26 μg of Amifloxacin per mL. From 0.75 to 4 h, blood radioactivity decreases rapidly from 7.0±0.25 μg/mL to 1.2±0.12 μg/mL. Between 8 and 48 h the rate of decline in blood radioactivity slows and is more complex. At 48 h, the blood radioactivity is equivalent to 0.14±0.02 μg/mL. Blood levels of radioactivity after i.v. administration of [14C]Amifloxacin mesylate to rats at 20 mg/kg decrease from 29.1±0.85 μg/mL at 1.0 min to 14.4±0.52 μg/mL at 10 min. From 0.25 to 4 h blood radioactivity decreases from 13.0±0.42 μg/mL to 0.97±0.09 μg/mL in a log-linear manner. The rate of elimination from 4 to 24 h is slower and more complex. At 24 h, blood radioactivity is equivalent to 0.12±0.01 ug/mL[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] In each study, groups of eight Sprague-Dawley rats (four per sex) are dosed either orally bygavage or intravenously via the jugular vein with [14C] Amifloxacin mesylate at 20 mg/kg. All doses are prepared as solutions in distilled water. Orally medicated animals are fasted overnight before dosing. Rats in absorption studies are held in restrainers while serial blood samples are collected from the tail vein into 50 μL heparinized capillary tubes. Rats in the excretion and distribution studies are maintained in individual metabolism cages. In the distribution study, groups of rats are killed at either 0.5 or 6.0 h, blood is collected from the abdominal aorta, and tissues and organs are dissected. |
| References |
| Density | 1.44g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 532.5ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19FN4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 334.34500 |
| Flash Point | 275.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 334.14400 |
| PSA | 77.81000 |
| LogP | 0.83980 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.662 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |