203806-08-0
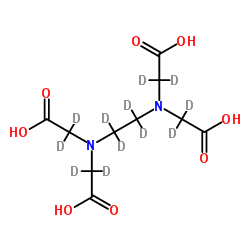
| Name | 2-[[2-[bis[carboxy(dideuterio)methyl]amino]-1,1,2,2-tetradeuterioethyl]-[carboxy(dideuterio)methyl]amino]-2,2-dideuterioacetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2,2',2'',2'''-[(H)Ethane-1,2-diyldinitrilo]tetra(H)acetic acid
2,2',2'',2'''-[(H)-1,2-Ethanediyldinitrilo]tetra(H)acetic acid Ethylenediaminetetraacetic-d12 acid MFCD00144285 EDTA-d12 |
| Description | EDTA-d12 is the deuterium labeled Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid[1]. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is a metal chelators (binds to metal divalent and trivalent cations including calcium), which shows activities of anticoagulant and anti-hypercalcemic. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid decreases the metal ion-catalyzed oxidative damage to proteins, and allows maintenance of reducing environment during protein purification. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid can also decrease the formation of disulfide bonds[2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 614.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 250ºC (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H4D12N2O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 304.317 |
| Flash Point | 325.2±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 304.165985 |
| PSA | 155.68000 |
| LogP | -0.43 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.580 |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |