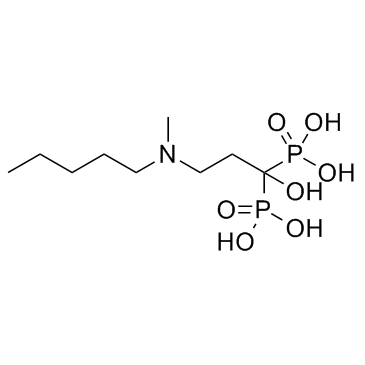
138844-81-2
| Name | Ibandronic Acid Sodium Salt |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Sodium hydrogen {1-hydroxy-3-[methyl(pentyl)amino]-1-phosphonopropyl}phosphonate
BM 21.0955Na boniva Natriumhydrogen-{1-hydroxy-3-[methyl(pentyl)amino]-1-phosphonopropyl}phosphonat Phosphonic acid, (1-hydroxy-3-(methylpentylamino)propylidene)bis-, monosodium salt SodiuM Ibandronate hydrogène {1-hydroxy-3-[méthyl(pentyl)amino]-1-phosphonopropyl}phosphonate de sodium Phosphonic acid, [1-hydroxy-3-(methylpentylamino)propylidene]bis-, sodium salt (1:1) phosphonic acid, [1-hydroxy-3-(methylpentylamino)propylidene]bis-, monosodium salt sodium,hydroxy-[1-hydroxy-3-[methyl(pentyl)amino]-1-phosphonopropyl]phosphinate Ibandronate sodium |
| Description | Ibandronate Sodium is a highly potent nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate used for the treatment of osteoporosis.Target: OthersIbandronate (1.25-2 μM) significantly reduces endothelial cell growth, while ibandronate (2 μM) also significantly reduces capillary-like tube formation and increases apoptosis of endothelial cells. Ibandronate (< 100 μM) dose-dependently increases VEGF expression in endothelial cells [1]. Ibandronate (< 100 μM) inhibits growth of both prostate cancer cell lines (LNCaP and PC-3) in a dose dependent manner [2].Ibandronate administered either daily (2.5 mg) or intermittently (20 mg every other day for 12 doses every 3 months) significantly reduces the risk of new morphometric vertebral fractures by 62% and 50% (p = 0.0006), respectively, in osteoporotic women after 3 years' treatment. Ibandronate administered either daily (2.5 mg) or intermittently (20 mg every other day for 12 doses every 3 months) significantly and progressively increases BMD of lumbar spine by 6.5% and 5.7%, respectively, in osteoporotic women after 3 years' treatment [3]. Ibandronate (< 125 mg/kg s.c.) results in a dose dependent increase in bone mineral density (BMD), trabecular bone volume and trabecular number, load to failure (Fmax), and yield load in long bones and vertebrae in ovariectomized rats, and increased trabecular separation in ovariectomized rats is fully prevented by all doses [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 587.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H22NNaO7P2 |
| Molecular Weight | 341.211 |
| Flash Point | 309.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 341.076904 |
| PSA | 160.98000 |
| LogP | 0.93820 |
| Appearance | white |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.88E-16mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: >10mg/mL |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| RTECS | SZ8563300 |
|
~% 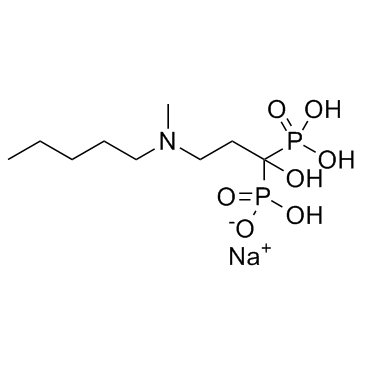
138844-81-2 |
| Literature: WO2006/2348 A2, ; Page/Page column 45 ; |