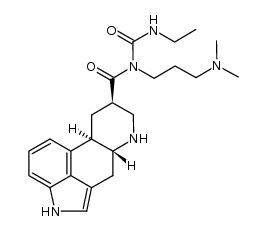
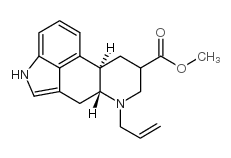
81409-90-7
| Name | cabergoline |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cabergolinum [Latin]
Cabergolina [Spanish] (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-en-1-yl-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]chinolin-9-carboxamid ergoline-8-carboxamide, N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-(2-propenyl)-, (8β)- (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-en-1-yl-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (8β)-6-Allyl-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)ergoline-8-carboxamide Cabaseril Galastop(R) Dostinex (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(diméthylamino)propyl]-N-(éthylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-én-1-yl-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoléine-9-carboxamide (8b)-N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-(2-propenyl)ergoline-8-carboxamide Cabaser (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide Dostinex(R) (8β)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-6-(prop-2-en-1-yl)ergoline-8-carboxamide Ergoline-8-carboxamide, N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-(2-propen-1-yl)-, (8β)- (8β)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-prop-2-en-1-ylergoline-8-carboxamide Cabergolinum 1-Ethyl-3-(3'-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-(6'-allylergoline-8'b-carbonyl)urea cabergolide N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-6-(2-propenyl)-8g-ergoline-8-carboxamide (8β)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-6-prop-2-en-1-ylergoline-8-carboxamide Cabergolina Galastop MFCD00867887 Cabergoline cabergolinum [INN_la] |
| Description | Cabergoline is an ergot derived-dopamine D2-like receptor agonist that has high affinity for D2, D3, and 5-HT2B receptors (Ki=0.7, 1.5, and 1.2, respectively). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 0.7 (Dopamine D2 receptor), 1.5 (Dopamine D3 receptor), 1.2 (5-HT2B receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | Cabergoline acts as a potent agonist of D2, D3 and 5-HT2B receptors. Pretreatment with Cabergoline inhibits H2O2-induced neuronal cell death in a dose-dependent manner. In the following experiments, 10 µM of Cabergoline is used to investigate its neuroprotective effects. MAP2 staining reveals that Cabergoline significantly suppresses the loss of neurons caused by H2O2 incubation. The detection of apoptotic nuclear condensation suggested that Cabergoline prevents apoptotic cell death following H2O2 exposure[1]. |
| In Vivo | Cabergoline has a longer elimination half-life (63 to 109 h) compared with other D2-like receptor agonists, both a long-lasting clinical effect following single-dose administration, and an improvement in the quality of life of patients with chronic diseases are expected[1]. The most significant reduction in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep bout number occurred during the light phase, in which Cabergoline-injected female handled mice has 67.3% less REM sleep bouts (F(1,11)=12.892, P=0.004) than Cabergoline-injected females that are restrained, although the greatest number in reduction of REM sleep bouts occurr during the dark phase (82.3% fewer REM sleep bouts; F(1,11)=3.667, P=0.082). In male mice, Cabergoline reduces baseline Prolactin (PRL) levels (98.5%; F(1,6)=13.192, P=0.011) from 5.8±1.3 to 0.08 ng/mL within 2 hours of injection. After a 7-day recovery period, PRL levels return to values that are not different from baseline (5.0±0.60 ng/mL; F(1,6)=0.715, P=0.43)[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Primary cortical neurons are prepared. Cabergoline (10 µM; except for experiments of dose-dependency) is applied to cortical cells at DIV 6-7. After 24-hour Cabergoline treatment (except for examination of pretreatment time-dependency of Cabergoline), H2O2 (50 µM; except for the dose-dependency of H2O2) is added. All inhibitors and antagonists, including spiperone, U0126, SB203580, SP600125, AP5, and nifedipine are applied 20 min before Cabergoline or H2O2 addition. L-glutamate is added at DIV 7-8 for cell death induction. Cell survival rate is measured by MTT assay. After the indicated treatment with drugs is completed, culture medium is replaced with 200 µL fresh medium containing 40 µl MTT solution (2.5 mg/mL, diluted in PBS) and cells are incubated at 37°C for 1.5-2.5 hours. Then, 200 µL lysis buffer containing isopropyl alcohol is applied to each well and mixed by pipetting. Each sample is moved to a 96-well plate and its absorbance at 570 nm is measured using an iMark Micro plate leader. Cell survival rate is quantitated by absorbance measurement, because MTT (yellow) is deoxidized to formazan (violet) in proportion to mitochondrial activity[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Female and male C57BL/6J mice are used.Cabergoline is dissolved in 100% pharmasolve and then diluted with 20% β-cyclodextrin in water to yield a final concentration of 0.15-0.5 mg/mL Cabergoline. Mice received a 0.3-mg/kg ip injection of Cabergoline or vehicle. All drugs are prepared within 48 hours of experiment and stored at 4°C. Solutions are allowed to reach at room temperature before injection. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 102-104°C |
| Molecular Formula | C26H37N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 451.604 |
| Exact Mass | 451.294739 |
| PSA | 71.68000 |
| LogP | 2.43 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.594 |
| Storage condition | Store at +4°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R37:Irritating to the respiratory system. R43:May cause sensitization by skin contact. |
| Safety Phrases | S8-S24/25-S46 |
| RIDADR | UN 2210 |
| RTECS | ZB3200000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
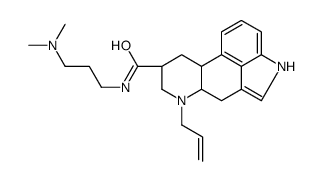
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
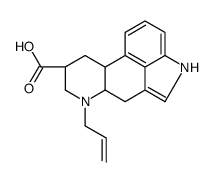
| DownStream 2 | |