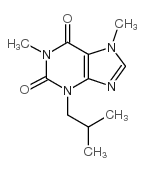
28822-58-4
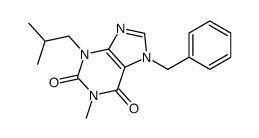
| Name | 3-isobutyl-1-methyl-7H-xanthine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3-Isobutyl-1-methyxanthine
3-Isobutyl-1-methyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 3-Isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1-methyl-3-(2-methylpropyl)- IBMX EINECS 249-259-3 Xanthine,3-isobutyl-1-methyl MFCD00005584 1-METHYL-3-ISOBUTYLXANTHINE 1-methyl-3-(2-methylpropyl)-7H-purine-2,6-dione 3-Isobutyl-1-methylxanthine isobutylmethylxanthine Methylisobutylxanthine Methylergometrine maleate 3-isobutylmethylxanthine 3-isobutyl-1-methyl-7H-xanthine NSC165960 SC2964 |
| Description | IBMX is a broad-spectrum phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor, with IC50s of 6.5, 26.3 and 31.7 μM for PDE3, PDE4 and PDE5, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 6.5±1.2 μM(PDE3), 26.3±3.9 μM (PDE4), 31.7±5.3 μM (PDE5)[1] |
| In Vitro | At 100 μM, KMUP-1 (a xanthine derivative) and IBMX are the most effective at inducing tracheal relaxation; the magnitude of the relaxation responses induced by KMUP-1 and IBMX are not significantly different[1]. IBMX (100 μM) activates renal outer medullary K+ (ROMK) channels (n=6, P<0.05) and prevents further channel activation by ANG II (n=6, P=NS) or cGMP. Of note is that pretreatment of cortical collecting duct (CCDs) isolated from high-K+ (HK)-fed rats with IBMX (100 μM) for 20 min leads to a significant increase in tubular cAMP content to 1.43±0.35 pg/mm tubule length (n=14) compare with that measured in vehicle-treated controls (0.61±0.13 pg/mm tubule length, n=12, P<0.05)[2]. |
| In Vivo | IBMX, a non-selective PDE inhibitor significantly decreases the liver glycogen storage (mg/g, IBMX 22±1.5 P<0.001). IBMX potentiates insulin release and in hepatocytes and adipocytes, they increase glycogenolysis and lipolysis. In comparison with the control group, IBMX and mc5 significantly increase plasma glucose (blood glucose, mg/dl, control=141±3, IBMX=210±17 P<0.001 and mc5=191±13 P<0.01) while other test compounds (mc1, mc6, MCPIP and milrinone) do not produce significant effect (control=141±3, mc1 160±7, mc6 175±9, MCPIP 179±8 and milrinone 116±2 P>0.05) also mc2 does not change plasma glucose (control=141±3 and mc2=145±5). IBMX has the highest efficacy on increasing plasma glucose[3]. Treatments with IBMX and Apocynin significantly decrease cold-induced elevation of right ventricular (RV) systolic pressure (23.5±1.8 and 24.2±0.6 mmHg, respectively) although they do not decrease RV pressure to the warm control levels. IBMX or Apocynin significantly reduces medial layer thickness (19.0±0.9, and 16.9±0.8 μm, respectively) and increases lumen diameter (62.7±4.2, and 59.5±4.3 μm, respectively) of small PAs in cold-exposed rats[4]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are grown in 24-well plates 105 cells per well. At confluence, monolayer cells are washed with phosphate buffer solution (PBS) and then incubated with KMUP-1 (0.1-100 μM) in the presence of 100 μM IBMX for 20 min. Incubation is terminated by the addition of 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA). Cell suspensions are sonicated and then centrifuged at 2500× g for 15 min at 4°C. To remove TCA, the supernatants are extracted three times with 5 volumes of water-saturated diethyl ether. Then, the supernatants are lyophilized and the cyclic GMP or AMP of each sample is determined by using commercially available radioimmunoassay kits[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Male mice (25-35 g) are used. For the experiment, the test compound (IBMX, milrinone, MCPIP, mc1, mc2, mc5 or mc6) or solvent (control) is injected subcutaneously to mice at 1 mg/kg dosage twice a day (8:00 a.m. and 8:00 p.m.) for 7 days. On day 8, animals are anesthetized with intraperitoneal injection of thiopental (80 mg/kg) and blood samples are obtained from their hearts and then the liver is dissected. Each sample is centrifuged for 5 min and its serum is separated. The serum and the liver of each animal are kept frozen in less than -18 oC for the following measurements. Rats[4] Six groups of male Sprague-Dawley rats are used (150-180g, 6 rats/group). Three groups of rats are exposed to a climate-controlled walk-in chamber maintained at moderate cold (5.0±1°C). The remaining groups are kept in an identical chamber maintained at room temperature (23.5±1°C, warm) and served as controls. After eight weeks of exposure to cold, 3 groups in each temperature condition received continuous IV infusion of IBMX (PDE-1 inhibitor, 8.5 mg/kg/day), Apocynin (NADPH oxidase inhibitor, 25 mg/kg/day) and vehicle (DMSO, 50%), respectively. The doses of drugs have been validated for effective inhibition of PDE-1 and NADPH oxidase activity, respectively. Body weight is measured weekly. After one week of drug infusion, the animals’ right ventricular systolic blood pressure (RVBP) is measured under anesthesia. The RVP is a reliable indicator of pulmonary arterial blood pressure (PAP) and has been used by numerous investigators for evaluating PH. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 445.6±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 200-201 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 222.244 |
| Flash Point | 223.3±26.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 222.111679 |
| PSA | 72.68000 |
| LogP | 1.24 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.569 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: 1 M with gentle warming |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | ZD8500000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|






![1-methyl-7-[(pivaloyloxy)methyl]xanthine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/241/69150-36-3.png)