24512-63-8
| Name | Geniposide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Olea europaea L
Methyl (1S)-1-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-7-(hydroxymethyl)-1,4a,5,7a-tetrahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylate Geniposide Geniposidic Jasminoidin Methyl (1S,4aS,7aS)-1-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-7-(hydroxymethyl)-1,4a,5,7a-tetrahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylate Genipin 1-glucoside MFCD00016659 |
| Description | Geniposide is an iridoid glucoside extracted from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis fruits; exhibits a varity of biological activities such as anti-diabetic, antioxidative, antiproliferative and neuroprotective activities. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Geniposide exhibits a variety of activities, such as on antithrombosis, anti-inflammation, anti-diabetes, anti-atherosclerosis, antidepression, healing Alzheimer’s disease (AD), anti-hypertension, toxicology, and untoward reaction are summarized[1]. Geniposide markedly declines the production of IL-8, IL-1β and MCP-1 in OGD-induced brain microvascular endothelial cells, the expression of P2Y14 receptor is significantly down-regulated, the phosphorylation of RAF-1, MEK1/2, ERK1/2 are suppressed[2]. |
| In Vivo | Geniposide (200 and 400 mg/kg) significantly decreases the blood glucose, insulin and TG levels in diabetic mice in a dose-dependent manner. This compound also decreases the expression of GP and G6Pase at mRNA and immunoreactive protein levels, as well as enzyme activity[3]. Geniposide (20.0, 40.0, or 80 mg/kg) significantly reverses the excessive, alcohol-induced elevation in both serum ALT/AST and hepatic LPO levels. Geniposide upregulates the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) to attenuate the cell apoptosis induced by 3-morpholinosydnonimine hydrochloride (SIN-1) in primary cultured hippocampal neurons[4]. Geniposide inhibits photochemistry-induced thromboembolism model in vivo. Geniposide are very effective depressants on NF-κB by interrupting IκB degradation[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The third passages of brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) are used for the experiment. The BMECs are divided into four groups: (1)normal control group: the normal cultured BMECs without treatment; (2)OGD group: the BMECs injured by OGD according to the above method; (3) geniposide group: the OGD-injured BMECs treated with 33.2 μg/mL geniposide for 6 h; (4)PTX group: the OGD-injured BMECs administrated with 100 ng/mL PTX. PTX, known as an inhibitor of Gi-coupled receptor is used to assess the activation of P2Y14 receptor induced by OGD in this experiment[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Type 2 diabetic mice, induced by a high-fat diet and streptozotocin injection, are treated with or without geniposide for 2 weeks. Blood glucose levels are monitored by a glucometer. Insulin concentrations are analyzed by the ELISA method. Total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) levels are measured using Labassay kits. Activities of hepatic GP and G6Pase are measured by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-coupled reaction. Real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting are used to determine the mRNA and protein levels of both enzymes[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 641.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 161-162ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C17H24O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 388.366 |
| Flash Point | 231.5±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 388.136932 |
| PSA | 155.14000 |
| LogP | -1.92 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±4.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.621 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3.0 |
|
~% 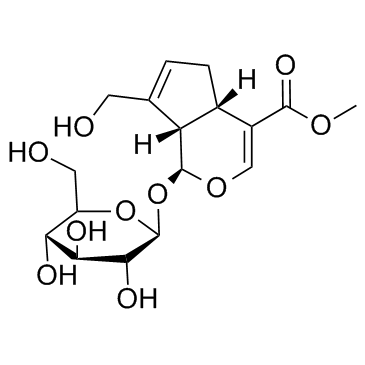
24512-63-8 |
| Literature: Organic Letters, , vol. 11, # 8 p. 1849 - 1851 |
|
~% 
24512-63-8 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 34, # 12 p. 4933 - 4938 |
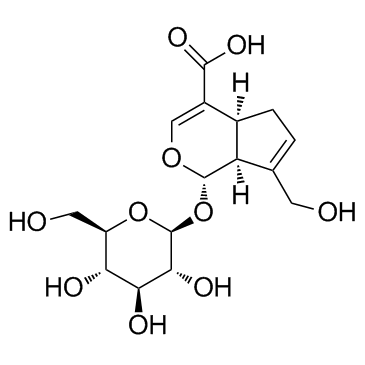
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |


![4,7-dimethyl-1,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-1-ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/386/109215-55-6.png)