CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
-
RTECS NUMBER :
-
YV8300000
-
CHEMICAL NAME :
-
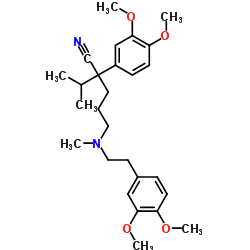
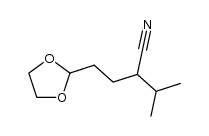
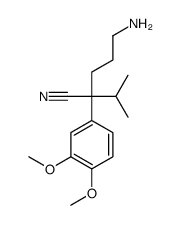
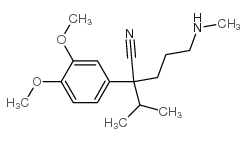
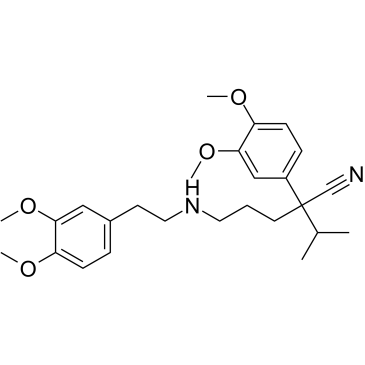
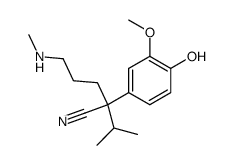
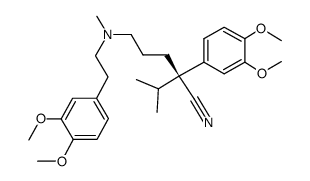
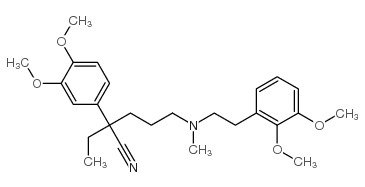
Valeronitrile, 5-((3,4-dimethoxyphenethyl)methylamino)-2-(3,4-dimeth oxyphenyl)-2-isopropy l-
-
CAS REGISTRY NUMBER :
-
52-53-9
-
LAST UPDATED :
-
199801
-
DATA ITEMS CITED :
-
19
-
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
-
C27-H38-N2-O4
-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
-
454.67
-
WISWESSER LINE NOTATION :
-
1OR BO1 DXCN&Y1&1&3N1&2R CO1 DO1
HEALTH HAZARD DATA
ACUTE TOXICITY DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
80 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - coma Cardiac - pulse rate increase, without fall in BP Vascular - BP lowering not characterized in autonomic section
-
REFERENCE :
-
HETOEA Human & Experimental Toxicology. (Macmillan Press Ltd., Brunel Road, Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire, RG21 2XS, UK) V.9- 1990- Volume(issue)/page/year: 16,35,1997
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
46 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Sense Organs and Special Senses (Eye) - ptosis Cardiac - EKG changes not diagnostic of specified effects Vascular - BP lowering not characterized in autonomic section
-
REFERENCE :
-
CTOXAO Clinical Toxicology. (New York, NY) V.1-18, 1968-81. For publisher information, see JTCTDW. Volume(issue)/page/year: 17,395,1980
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
2 gm/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Sense Organs and Special Senses (Olfaction) - effect, not otherwise specified Cardiac - other changes Vascular - BP lowering not characterized in autonomic section
-
REFERENCE :
-
CHETBF Chest. (American College of Chest Physicians, 911 Busse Hwy, Park Ridge, IL 60068) V.57- 1970- Volume(issue)/page/year: 75,200,1979
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
64 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Cardiac - pulse rate Cardiac - change in rate Vascular - BP lowering not characterized in autonomic section
-
REFERENCE :
-
BMJOAE British Medical Journal. (British Medical Assoc., BMA House, Tavistock Sq., London WC1H 9JR, UK) V.1- 1857- Volume(issue)/page/year: 2,1127,1978
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
48 mg/kg/2W-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Liver - hepatitis (hepatocellular necrosis), diffuse
-
REFERENCE :
-
NEJMAG New England Journal of Medicine. (Massachusetts Medical Soc., 10 Shattuck St., Boston, MA 02115) V.198- 1928- Volume(issue)/page/year: 306,612,1982
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
83 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Cardiac - cardiomyopathy including infarction Vascular - BP lowering not characterized in autonomic section
-
REFERENCE :
-
AJEMEN American Journal of Emergency Medicine. (WB Saunders, Philadelphia, PA) V.1- 1983- Volume(issue)/page/year: 7,624,1989
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
3429 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Cardiac - pulse rate Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - acute pulmonary edema
-
REFERENCE :
-
CCMDC7 Critical Care Medicine. (Williams & Wilkins, 428 E. Preston Street, Baltimore, MD 21202) V.1- 1973- Volume(issue)/page/year: 19,436,1991
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
1429 ug/kg/5M-C
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Cardiac - pulse rate Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - cyanosis Skin and Appendages - sweating
-
REFERENCE :
-
NEJMAG New England Journal of Medicine. (Massachusetts Medical Soc., 10 Shattuck St., Boston, MA 02115) V.198- 1928- Volume(issue)/page/year: 306,238,1982
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
71 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Cardiac - pulse rate increase, without fall in BP Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - dyspnea
-
REFERENCE :
-
AHJOA2 American Heart Journal. (C.V. Mosby Co., 11830 Westline Industrial Dr., St. Louis, MO 63146) V.1- 1925- Volume(issue)/page/year: 111,622,1986
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - child
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
250 ug/kg/5M-C
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Cardiac - arrhythmias (including changes in conduction)
-
REFERENCE :
-
AHJOA2 American Heart Journal. (C.V. Mosby Co., 11830 Westline Industrial Dr., St. Louis, MO 63146) V.1- 1925- Volume(issue)/page/year: 106,145,1983
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
163 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
EJMCA5 European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry--Chimie Therapeutique. (Editions Scientifiques Elsevier, 29 rue Buffon, F-75005, Paris, France) V.9- 1974- Volume(issue)/page/year: 25,351,1990
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
7250 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
PCJOAU Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal (English Translation). Translation of KHFZAN. (Plenum Pub. Corp., 233 Spring St., New York, NY 10013) No.1- 1967- Volume(issue)/page/year: 22,123,1988
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
130 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
FATOAO Farmakologiya i Toksikologiya (Moscow). For English translation, see PHTXA6 and RPTOAN. (V/O Mezhdunarodnaya Kniga, 113095 Moscow, USSR) V.2- 1939- Volume(issue)/page/year: 54(2),40,1991
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
43 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
JDGRAX Journal of Drug Research. (National Organization for Drug Research and Control, POB 29, Cairo, Egypt) V.2- 1969- Volume(issue)/page/year: 15(1-2),121,1984
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Subcutaneous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
30770 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
JPPMAB Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. (Pharmaceutical Soc. of Great Britain, 1 Lambeth High St., London SEI 7JN, UK) V.1- 1949- Volume(issue)/page/year: 34,329,1982
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
1520 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
EJTXAZ European Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Hygiene. (Paris, France) V.7-9, 1974-76. For publisher information, see TOERD9. Volume(issue)/page/year: 8,188,1975 ** REPRODUCTIVE DATA **
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
DOSE :
-
51 mg/kg
-
SEX/DURATION :
-
male 30 day(s) pre-mating
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Reproductive - Paternal Effects - breast development
-
REFERENCE :
-
MJAUAJ Medical Journal of Australia. (Australasian Medical Pub. Co. Ltd., 71-79 Arundel St., Glebe, N.S.W., Australia) V.1- 1914- Volume(issue)/page/year: 161,328,1994
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
DOSE :
-
60 mg/kg
-
SEX/DURATION :
-
female 10-12 day(s) after conception
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Reproductive - Fertility - post-implantation mortality (e.g. dead and/or resorbed implants per total number of implants) Reproductive - Effects on Embryo or Fetus - fetotoxicity (except death, e.g., stunted fetus) Reproductive - Specific Developmental Abnormalities - cardiovascular (circulatory) system
-
REFERENCE :
-
REPTED Reproductive Toxicology. (Pergamon Press Inc., Maxwell House, Fairview Park, Elmsford, NY 10523) V.1- 1987- Volume(issue)/page/year: 11,207,1997 *** NIOSH STANDARDS DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE DATA *** NIOSH OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE SURVEY DATA : NOES - National Occupational Exposure Survey (1983) NOES Hazard Code - X4662 No. of Facilities: 65 (estimated) No. of Industries: 1 No. of Occupations: 2 No. of Employees: 14268 (estimated) No. of Female Employees: 7372 (estimated)
|