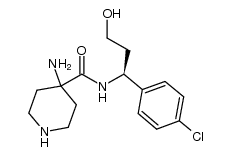
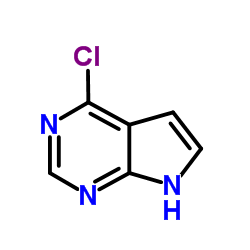
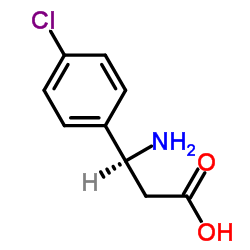
1143532-39-1
| Name | 4-amino-N-[(1S)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-1-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
4-Piperidinecarboxamide, 4-amino-N-[(1S)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-1-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-
4-Amino-N-[(1S)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-1-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-4-piperidinecarboxamide cc-638 AZD5363 UNII-WFR23M21IE CS-1284 AZD-5363 |
| Description | Capivasertib (AZD5363) is a potent pan-AKT kinase inhibitor with IC50 of 3, 7 and 7 nM for Akt1,Akt2 and Akt3, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Akt1:3 nM (IC50) Akt2:7 nM (IC50) Akt3:7 nM (IC50) ROCK2:60 nM (IC50) ROCK1:470 nM (IC50) PKA:7 nM (IC50) P70S6K:6 nM (IC50) Autophagy |
| In Vitro | Capivasertib, a novel pyrrolopyrimidine-derived compound, inhibits all AKT isoforms with a potency of 10 nM or less and inhibits phosphorylation of AKT substrates in cells with a potency of approximately 0.3 to 0.8 μM. Capivasertib inhibits phosphorylation of these substrates with an IC50 value of 0.06 to 0.76 μM in the 3 cell lines. Capivasertib effectively inhibits phosphorylation of S6 and 4E-BP1 in these cell lines, whereas it increases phosphorylation of AKT at both ser473 and thr308. In BT474c cells, Capivasertib induces FOXO3a nuclear translocation with EC50 value of 0.69 μM; a concentration of 3 μM is sufficient to almost completely localize FOXO3a to the nucleus. AZD5363Capivasertibhibitor MK-2206 is much less active (IC50>30 μM)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Oral dosing of Capivasertib (AZD5363) to nude mice causes dose- and time-dependent reduction of PRAS40, GSK3β, and S6 phosphorylation in BT474c xenografts (PRAS40 phosphorylation EC50 ~0.1 μM total plasma exposure), reversible increases in blood glucose concentrations, and dose-dependent decreases in 2[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (18F-FDG) uptake in U87-MG xenografts. Chronic oral dosing of Capivasertib caused dose-dependent growth inhibition of xenografts derived from various tumor types, including HER2+ breast cancer models that are resistant to trastuzumab. Capivasertib also significantly enhances the antitumor activity of docetaxel, lapatinib, and trastuzumab in breast cancer xenografts[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Cell proliferation assay is determined by 2 methods, MTS and Sytox Green. Briefly, cells are seeded in 96-well plates (at a density to allow for logarithmic growth during the 72-hour assay) and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. Cells are then exposed to concentrations of Capivasertib ranging from 30 to 0.003 μM for 72 hours. For the MTS endpoint, cell proliferation is measured by the CellTiter AQueous Non-Radioactive Cell Proliferation Assay reagent. Absorbance is measured with a Tecan Ultra instrument. For the Sytox Green endpoint, Sytox Green nucleic acid dye diluted in TBS-EDTA buffer is added to cells (final concentration of 0.13 μM) and the number of dead cells detected using an Acumen Explorer. Cells are then permeabilized by the addition of saponin (0.03% final concentration, diluted in TBS-EDTA buffer), incubated overnight and a total cell count measured. Predose measurements are made for both MTS and Sytox Green endpoints, and concentration needed to reduce the growth of treated cells to half that of untreated cells (GI50) values are determined using absorbance readings (MTS) or live cell counts[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Specific, pathogen-free, female nude mice (nu/nu: Alpk) and male SCID mice (SCID/CB17; 786-0 xenograft studies) are used. When mean tumor sizes reach approximately 0.2 cm3, the mice are randomized into control and treatment groups. The treatment groups received varying dose schedules of Capivasertib (AZD5363) solubilized in a 10% DMSO 25% w/v Kleptose HPB (Roquette) buffer by oral gavage, Docetaxel solubilized in 2.6% ethanol in injectable water by intravenous injection once on day 1 at 15 or 5 mg/kg once weekly. When administered in combination, Docetaxel is administered 1 hour before the oral dose of Capivasertib (AZD5363). The control group received the DMSO/Kleptose buffer alone, twice daily by oral gavage. Tumor volumes (measured by caliper), animal body weight, and tumor condition are recorded twice weekly for the duration of the study. Mice are sacrificed by CO2 euthanasia. The tumor volume is calculated (taking length to be the longest diameter across the tumor and width to be the corresponding perpendicular diameter) using the formula: (length×width)×√(length×width)×(π/6). Growth inhibition from the start of treatment is assessed by comparison of the differences in tumor volume between control and treated groups. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H25ClN6O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 428.915 |
| Exact Mass | 428.172760 |
| PSA | 123.65000 |
| LogP | 1.04 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.670 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|
|
~42% 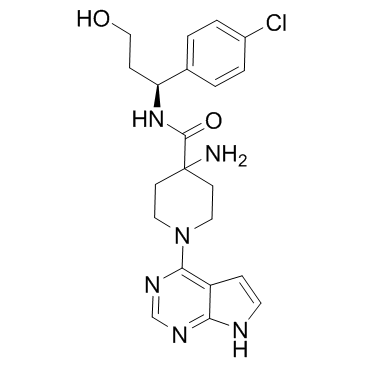
1143532-39-1 |
| Literature: ASTRAZENECA AB; ASTRAZENECA UK LIMITED Patent: WO2009/47563 A1, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 40 ; WO 2009/047563 A1 |
|
~19% 
1143532-39-1 |
| Literature: ASTRAZENECA AB; ASTRAZENECA UK LIMITED Patent: WO2009/47563 A1, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 39 ; WO 2009/047563 A1 |
|
~% 
1143532-39-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 56, # 5 p. 2059 - 2073 |
|
~% 
1143532-39-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 56, # 5 p. 2059 - 2073 |
|
~% 
1143532-39-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 56, # 5 p. 2059 - 2073 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |