304-55-2
| Name | succimer |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Butanedioic acid, 2,3-dimercapto-
(2R,3S)-rel-2,3-Dimercaptosuccinic acid Butanedioic acid, 2,3-dimercapto-, (R*,S*)- meso-2,3-diisopropyl-succinic acid 2,3-Disulfanylsuccinic acid 3-dimercaptosuccinic acid meso-2,3-Dimercaptosuccinic acid Succinic acid, 2,3-dimercapto-, (±)- meso-2,3-dimercapto succinic acid Dimercaptosuccinic acid meso-dimercaptosuccinic acid 2,3-disulfanylbutanedioic acid EINECS 206-155-2 MFCD00064799 meso-2,3-Diisopropyl-bernsteinsaeure Succimer 2,3-DIISOPROPYLSUCCINIC ACID 2,3-Dithio-meso-tartaric acid |
| Description | Succimer is a widely used chelating agent for the treatment of Pb poisoning. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Succimer is a widely used chelating agent for the treatment of Pb poisoning. Red blood cells (RBCs) from lead exposed animals treated with NAC or Succimer are shown to have significantly higher glutathione (GSH) levels and diminished malondialdehyde (MDA) levels when compare to the lead group. Succimer administration also results in decreased glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity in RBCs from lead exposed animals[1]. Succimer treatment produces a significant reduction in blood lead levels for both lead exposure conditions: the High Pb-succ group has blood lead levels that are 27% of the blood lead levels of the High Pb group at the end of treatment. Succimer is effective in substantially reducing brain lead, as brain lead levels in the High Pb-succ group are 37% of levels in the High Pb group[2]. |
| Animal Admin | All experiments are performed with Fisher 344 male rats weighing 75 to 100 g. The animals are randomized into four groups. Group I (n=11) serves as the control and is given only standard rat chow and water for 6 weeks. Group II (n=11) receives 2000 ppm lead acetate in its drinking water for 5 weeks and, during the 6th week, this group receives water. Group III (n=6) receives 2000 ppm lead acetate in its drinking water for 5 weeks and, during the 6th week, these animals receive 800 mg/kg/day NAC dissolved in water. Group IV (n=6) is treated like group III, except that it receives 90 mg/kg/day Succimer during the last week. At the end of the 6th week, after overnight fasting, the animals are anesthetized with metofane and blood samples are collected via intracardiac puncture using heparin as an anticoagulant. Plasma and the buffy coat are removed by centrifugation for 10 min at 3000 rpm. The RBCs are washed three times with an equal volume of cold saline[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 267.6±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 196-198ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O4S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.218 |
| Flash Point | 115.6±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 181.970749 |
| PSA | 152.20000 |
| LogP | 1.93 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.617 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25-26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | WM7650000 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|
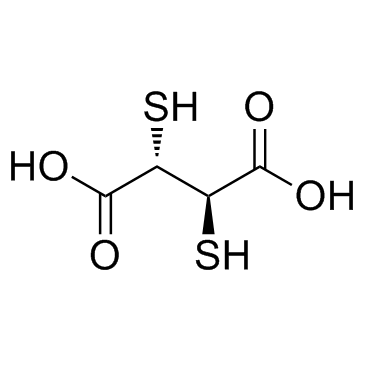
~% 
304-55-2 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 44, p. 955 - 960 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |


