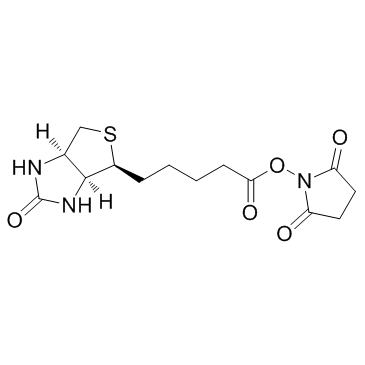
875770-34-6
| Name | 5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]-N-[2-[2-[2-(2-azidoethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]pentanamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1H-Thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanamide, N-[2-[2-[2-(2-azidoethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]hexahydro-2-oxo-, (3aS,4S,6aR)-
Biotin-PEG3-Azide N-(2-{2-[2-(2-Azidoethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy}ethyl)-5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanamide |
| Description | Biotin-PEG3-azide is a PEG-based PROTAC linker can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PEGs |
| In Vitro | Biotin-C2-PEG3-azide is a biotin with the azide tag, it can be conjugated to antiviral inhibitors, for example, RYL-634, which shows excellent broad-spectrum inhibition activity against various pathogenic viruses, including hepatitis C virus, dengue virus, Zika virus, chikungunya virus, enterovirus[1]. PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 110 °C |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H32N6O5S |
| Molecular Weight | 444.549 |
| Exact Mass | 444.215485 |
| PSA | 179.95000 |
| LogP | -0.93 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~75% 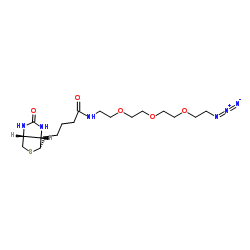
875770-34-6 |
| Literature: THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL; KOHN, Harold, L.; PARK, Ki Duk Patent: WO2010/14236 A2, 2010 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 35 ; |
|
~89% 
875770-34-6 |
| Literature: Tantama, Mathew; Lin, Wan-Chen; Licht, Stuart Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008 , vol. 130, # 47 p. 15766 - 15767 |
|
~60% 
875770-34-6 |
| Literature: Yun, Wang; Shougang, Hu; Fast, Walter Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009 , vol. 131, # 42 p. 15096 - 15097 |
|
~97% 
875770-34-6 |
| Literature: Tae, Hyun Seop; Hines, John; Schneekloth, Ashley R.; Crews, Craig M. Organic Letters, 2010 , vol. 12, # 19 p. 4308 - 4311 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |