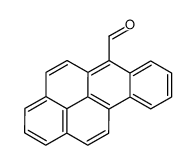
50-32-8
| Name | benzo[a]pyrene |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII-3417WMA06D
Benzo[a]pyrene (Ames grade) Benzo[A]Pyrene Benzo(d,e,f)chrysene Benzo(a)pyrene Benzo[a]pyren benzo[1,2,5]thiadiazole-4-sulfonyl chloride 2,1,3-benzothiadiazol-4-sulfonyl chloride 3,4-Benzpyrene 3,4-Benz(a)pyrene 4,5-BENZPYRENE 2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole,4-chlorosulfonyl 3,4-benzopyrene 2,1,3-benzothiadiazole-4-sulphonyl chloride 1,2-Benzpyrene (VAN) Benzo[pqr]tetraphene Benzopyrene 4-Chlorosulfonyl-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole 2,1,3-benzothiadiazole-4-sulfonylchloride 3,4-Benzo(a)pyrene Benzo-2,1,3-thiadiazole-4-sulphonyl chloride Benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-4-sulfonyl chloride EINECS 200-028-5 benz[a]pyrene benzo[2,1,3]thiadiazole-4-sulfonyl chloride 6,7-Benzopyrene MFCD00003602 1,2-Benzpyrene |
| Description | Benzo[a]pyrene shows lung carcinogenicity in animal models, and it is frequently used in chemoprevention studies. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Statistically significant decrease is observed at 7 weeks in females receiving 1.0 mg Benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) compare with the vehicle group. As lung tumorigenesis induced by Benzo[a]pyrene is dose dependent in female A/J mice. The incidence of hyperplasia values in females treating with 0.25, 0.50, and 1.0 mg Benzo[a]pyrene are significantly higher than in the vehicle-treated group. The incidence of adenoma in females receiving 1.0 mg Benzo[a]pyrene is significantly higher than in the vehicle group. The multiplicity of hyperplasia in females receiving 0.50 or 1.0 mg Benzo[a]pyrene is significantly higher than in the vehicle group. The multiplicity of adenoma in the group treated with 1.0 mg is also significantly higher than in the vehicle group. The incidences of hyperplasia and adenoma in female A/J mice are significantly increased by Benzo[a]pyrene in a dose-dependent manner[1]. Benzo[a]pyrene induces an average of 9.38±1.75 tumors with an average tumor load of 19.53±3.81 mm3 (P<0.05 compare to control). Benzo[a]pyrene administration significantly (P<0.05) decreases cAMP levels in tumors with adjacent lung tissues. The expression level of PDE4D gene is also increased by Benzo[a]pyrene administration[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Female A/J mice are randomized into eight groups (n=8): (i) control; (ii)Benzo[a]pyrene (B(a)P)+vehicle (methocel); (iii) Benzo[a]pyrene+roflumilast 1 mg/kg; (iv) Benzo[a]pyrene+roflumilast 5 mg/kg; (v) Benzo[a]pyrene+aerozolie phosphate-buffer saline (PBS); (vi) Benzo[a]pyrene+aerosolize budesonide 2.25 mg/mL; (vii) Benzo[a]pyrene+aerosolized budesonide 2.25 mg/mL+roflumilast 1 mg/kg; and (viii) Benzo[a]pyrene+aerosolize budesonide 2.25 mg/mL+roflumilast 5 mg/kg groups. A single dose of Benzo[a]pyrene in corn oil is given intraperitoneally once at 100 mg/kg body weight. Roflumilast (1 or 5 mg/kg) is started 2 weeks after Benzo[a]pyrene. It is continued for 26 weeks (3 days/week) via oral gavage. Mice in the Benzo[a]pyrene+vehicle group are treated with an equal volume of methocel as solvent control. Aerosolizing budesonide is administrated by inhaling route as an aerosol at a dose of 2.25 mg/mL for 2 min per application at 2 weeks after Benzo[a]pyrene. It is continued for 26 weeks (5 days/week). PBS is also used as solvent control by inhaling route after Benzo[a]pyrene administration in the Benzo[a]pyrene+PBS group. Mice are killed at 28 weeks after exposure to Benzo[a]pyrene. Their lungs are excised and stored at -70 °C[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 495.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 177-180°C |
| Molecular Formula | C20H12 |
| Molecular Weight | 252.309 |
| Flash Point | 228.6±13.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 252.093903 |
| LogP | 6.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.887 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H340-H350-H360FD-H410 |
| Supplemental HS | Repeated exposure may cause skin dryness or cracking. |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P273-P280-P308 + P313-P333 + P313-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F:Flammable;T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R45;R11;R38;R50/53;R65;R67 |
| Safety Phrases | S45-S53-S61-S60-S26-S62 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| RTECS | DJ3675000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2902909090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2902909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2902909090 other aromatic hydrocarbons。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:2.0%。General tariff:30.0% |

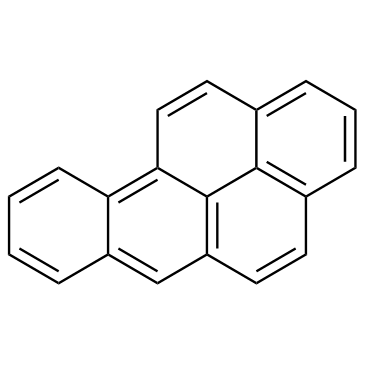
![9,10-dihydrobenzo[a]pyrene structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/421/17573-15-8.png)
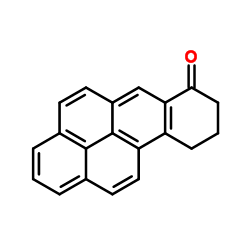
![7,8,9,10-Tetrahydrobenzo[pqr]tetraphen-7-ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/338/6272-55-5.png)
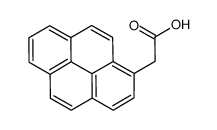
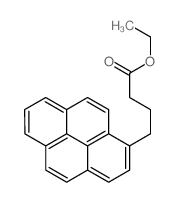
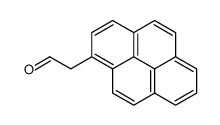
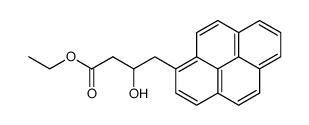


![6-Chlorobenzo[pqr]tetraphene structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/463/21248-01-1.png)
![3-Methoxy Benzo[a]pyrene structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/250/63059-68-7.png)