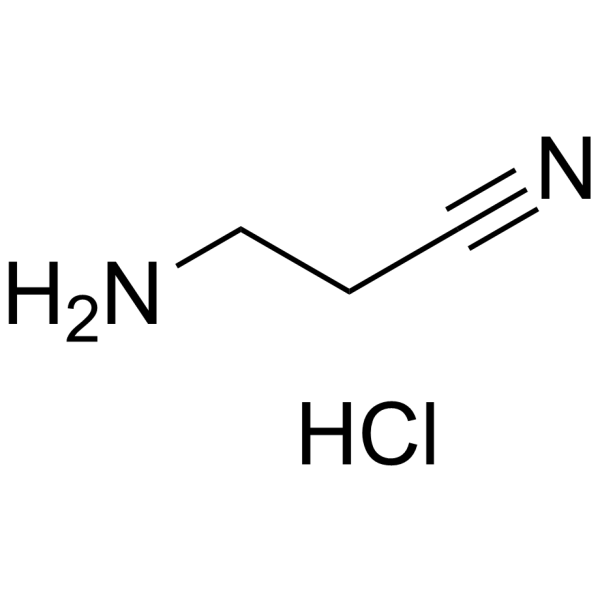
646-03-7
| Name | 3-aminopropanenitrile,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3-aminopropanenitrile hydrochloride |
| Description | β-Aminopropionitrile (BAPN) hydrochloride is a specific, irreversible and orally active lysyl oxidase (LOX) inhibitor. β-Aminopropionitrile hydrochloride targets the active site of LOX or LOXL isoenzymes[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite Lysyl Oxidase |
| In Vitro | β-Aminopropionitrile (BAPN) normalizes the expression of GLUT4 and adiponectin, and improves glucose uptake in an in vitro model of insulin resistance[1]. β-Aminopropionitrile (500 μM, 72 h) blocks the hypoxia-induced EMT morphological and marker protein changes, and inhibits invasion and migration capacities of cervical carcinoma cells in vitro[2]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: 3T3-L1 adipocytes Concentration: 200 μM with 1.15 nM and 2.87 nM TNFα Incubation Time: 72 h Result: TNFα reduced expression of GLUT4 and adiponectin, and increased SOCS3 protein levels in these cells. And these effects were prevented. Cell Invasion Assay[2] Cell Line: HeLa and SiHa cells Concentration: 500 μM Incubation Time: 72 h Result: Significantly reduced hypoxia-elicited cell invasion in both cell models. Cell Migration Assay [2] Cell Line: HeLa and SiHa cells Concentration: 500 μM Incubation Time: 72 h Result: Decreased hypoxia-induced migration from 180 and 240% to 60 and 70% in HeLa and SiHa cells, respectively. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: HeLa and SiHa cells Concentration: 500 μM Incubation Time: 72 h Result: Effectively prevented hypoxia-induced downregulation of E-cadherin and strongly inhibited hypoxia-induced upregulation of α-SMA and vimentin. |
| In Vivo | β-Aminopropionitrile (BAPN) (100 mg/kg/day; p.o.; 6 weeks) reduces body weight gain and improves the metabolic profile in diet-induced obesity in rats[1]. β-Aminopropionitrile monofumarate (1 g/kg/day; p.o.; 4 weeks) induces thoracic aortic dissection in C57BL/6 mice[3]. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats of 150 g, high-fat diet (HFD) model[1] Dosage: 100 mg/kg/day Administration: In the drinking water, 6 weeks Result: Significantly prevented the rise in body weight in HFD rats, but not in animals that were fed a standard diet. Reduced the increase in the weight of white adipose tissue (both epididymal and lumbar) in obese animals and attenuated their enhanced adiposity. Improved fasted glucose and insulin levels and consequently reduced HOMA index in the HFD group. Improved insulin signalling in adipose tissue from obese animals. Animal Model: C57BL/6 mice[3] Dosage: 1 g/kg/day Administration: In the drinking water, 4 weeks Result: Induce thoracic aortic dissection (TAD) in all mice with 24 h of Ang II infusion. Caused 87% of C57BL/6 mice to develop TAD without Ang II. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7ClN2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 106.55400 |
| Exact Mass | 106.03000 |
| PSA | 49.81000 |
| LogP | 1.36108 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |