100324-81-0
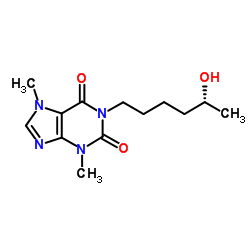
| Name | 1-[(5R)-5-hydroxyhexyl]-3,7-dimethylpurine-2,6-dione |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
R-1-(5-Hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine
(R)-3,7-Dihydro-1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione Lisophylline ProTec 1-[(5R)-5-Hydroxyhexyl]-3,7-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione Lisofylline 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethyl-, (R)- 1-[(R)-5-Hydroxyhexyl]theobromine CT 1501R CT-1501R 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1-[(5R)-5-hydroxyhexyl]-3,7-dimethyl- |
| Description | (R)-Lisofylline ((R)-Lisophylline) is a (R)-enantiomer of the metabolite of Pentoxifylline with anti-inflammatory properties. (R)-Lisofylline is a lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.6 µM and interrupts IL-12 signaling-mediated STAT4 activation. (R)-Lisofylline has the potential for type 1 diabetes, autoimmune disorders research[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.6 µM (Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase)[1] STAT4[1] |
| In Vitro | (R)-Lisofylline blocks IL-12-driven Th1 differentiation and T cell proliferation in vitro, yet has no effect on IL-12 secretion from APCs ex vivo or in vitro[3]. |
| In Vivo | (R)-Lisofylline reduces the impairment of insulin secretion induced by IL-1β in cultured rat islet cells, suppresses IFN-γ production, the onset of diabetes, and macrophage infiltration into islets from NOD mice, as well as Lisofylline improves insulin response and lowers glucose levels in Streptozotocin-treated rats after the oral glucose tolerance test[1]. (R)-Lisofylline prevents β cell dysfunction in NOD mice by inhibition of STAT4 phosphorylation which interrupts IL-12 signaling. (R)-Lisofylline ameliorates experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice[1]. (R)-Lisofylline also improves survival in mice injected with a lethal dose of LPS and ameliorates sepsis-induced lung injury in minipigs. In rats given IL-1 intratracheally (R)-Lisofylline pretreatment reduces lung leak but does not decrease neutrophil accumulation in lungs[1]. (R)-Lisofylline also suppresses release of TNF-α in vivo in mice and ex vivo in human blood stimulated with endotoxin derived from Salmonella or Escherichia coli[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 511.2±56.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C13H20N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 280.323 |
| Flash Point | 263.0±31.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 280.153534 |
| PSA | 82.05000 |
| LogP | 0.34 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.621 |