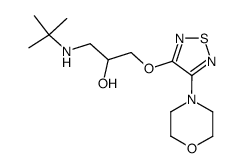
26839-75-8
| Name | (S)-timolol (anhydrous) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(S)-thymolol
timolol Istalol (S)-timolol (2S)-1-(tert-butylamino)-3-[(4-morpholin-4-yl-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)oxy]propan-2-ol Optimol (S)-(-)-3-(3-tert-butylamino-2-hydroxypropoxy)-4-(N-morpholino)-1,2,5-thiadiazole Timacar (S)-(-)-(1-tert-butylamino)-3-(4-morpholino-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yloxy)-2-propanol Timoptic Blocadren S(-)-Timolol maleate Betimol Timoptol EINECS 248-032-6 MFCD00864565 Timopic |
| Description | Timolol is a β-blocker available for both topical and systemic administration. Topical Timolol is primarily used to reduce intraocular pressure with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Timolol can also be used for the research of infantile hemangiomas, hypertension, myocardial infarction, migraine prophylaxis, and atrial fibrillation.Timolol also has cardioprotective effect[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Timolol can significantly prevent the increased lipid peroxidation level of the heart from diabetic rats. Timolol can induce a well-balanced ratio between oxidative stress and antioxidant defense system in the diabetic animals, can have an important cardioprotection against diabetes-induced ERS and associated apoptotic effects[3]. |
| In Vivo | Timolol has a cardioprotective effect via inhibition of ERS response in diabetic rats[3]. Animal Model: Experimental diabetes model: 3-month old male Wistar rats[3]. Dosage: 5 mg/kg Administration: Timolol (5 mg/kg daily for 12-week) Result: Showed cardioprotective effect. |
| References |
| Density | 1.224 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 487.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 71.5 - 72.5ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C13H24N4O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 316.42000 |
| Flash Point | 248.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 316.15700 |
| PSA | 107.98000 |
| LogP | 0.95840 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.62E-10mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.548 |
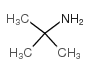
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
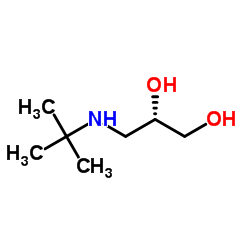
| DownStream 1 | |


![[(5S)-3-tert-butyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl]methanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/498/194861-99-9.png)
![rac 4-[4-(Oxiranylmethoxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]morpholine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/270/58827-68-2.png)
![(S)-4-[4-(Oxiranylmethoxy)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]morpholine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/376/69500-53-4.png)