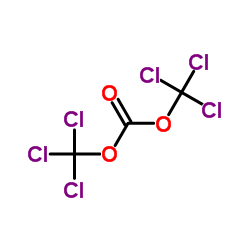
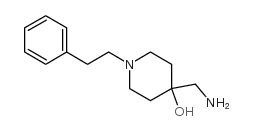
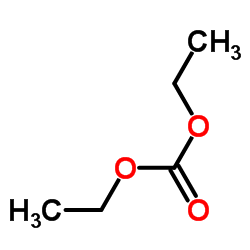
5053-06-5
| Name | 8-(2-phenylethyl)-1-oxa-3,8-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-2-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
8-phenethyl-1-oxa-3,8-diaza-spiro[4.5]decan-2-one
1-Oxa-3,8-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-2-one, 8-(2-phenylethyl)- Fluiden Fenspiridum [INN-Latin] Fenspiride [INN] EINECS 225-751-3 Viarespan 1-Oxa-3,8-diazaspiro[4.5]dec-2-en-2-ol, 8-(2-phenylethyl)- 8-(2-Phenylethyl)-1-oxa-3,8-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-2-one Fenspiride Respiride Fenspirida [INN-Spanish] |
| Description | Fenspiride, an orally active non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent, is an antagonist of H1-histamine receptor. Fenspiride inhibites phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3), phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) and phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) activities with -log IC50 values of 3.44, 4.16 and approximately 3.8, respectively. Fenspiride can be used for the research of respiratory diseases[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
-log IC50: 3.44 (PDE3); 4.16 (PDE4); approximately 3.8 (PDE5)[2] |
| In Vitro | Fenspiride (around 100 μM) inhibits histamine-induced contraction of isolated guinea pig trachea[2]. Fenspiride (≤1000 μM) produces less than 25% inhibition of phosphodiesterase 1 and phosphodiesterase 2 activities[2]. |
| In Vivo | Fenspiride (60 mg/kg; p.o. for 3 days) reduces the lipopolysaccharide-induced early rise of tumor necrosis factor concentrations in serum and in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of the model of endotoxemia[3]. Fenspiride (60 mg/kg; p.o. for 3 days) reduces the lipopolysaccharide-induced primed stimulation of alveolar macrophages[3]. Fenspiride (60 mg/kg; p.o. for 3 days) reduces the increased serum concentrations of extracellular type II phospholipase A 2, the intensity of the neutrophilic alveolar invasion and the lethality due to the lipopolysaccharide[3]. Animal Model: Lipopolysaccharide-treated Male Dunkin-Hartley guinea-pigs weighing 400-600 g[3] Dosage: 60 mg/kg Administration: orally for 3 days; pretreated Result: Reduced the lipopolysaccharide-induced early rise of tumor necrosis factor concentrations in serum (4.2 vs. 2.3 ng/ml) and in the BALF (55.7 vs. 19.7 ng/ml). Reduced the lipopolysaccharide-induced primed stimulation of alveolar macrophages, (1551.5 vs 771.5 pg/μg protein, P<0.05 for thromboxane B2 and 12.6 vs. 3.6 pg/μg protein, P<0.05 for leukotriene C4). Reduced the increased serum concentrations of extracellular type II phospholipase A 2 (3.9 vs. 1.2 nmol/ml per min), the intensity of the neutrophilic alveolar invasion and the lethality due to the lipopolysaccharide. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 408.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C15H20N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 260.332 |
| Flash Point | 200.7±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 260.152466 |
| PSA | 41.57000 |
| LogP | 1.91 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.609 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|
|
~69% 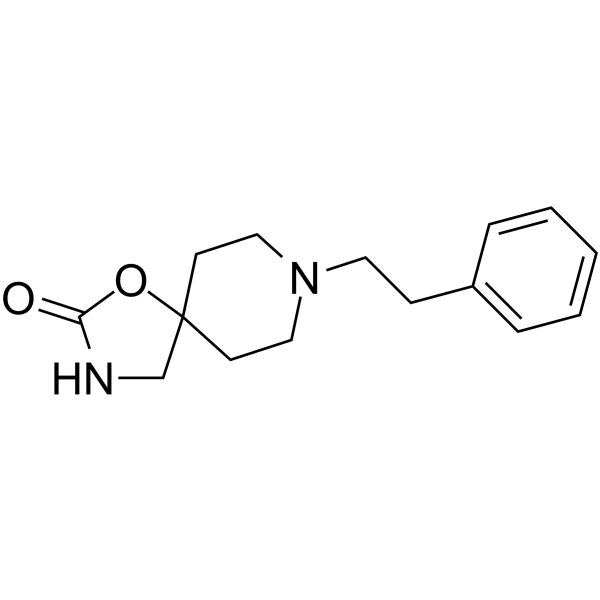
5053-06-5 |
| Literature: Somanathan; Rivero; Nunez; Hellberg Synthetic Communications, 1994 , vol. 24, # 10 p. 1483 - 1487 |
|
~% 
5053-06-5 |
| Literature: Synthetic Communications, , vol. 24, # 10 p. 1483 - 1487 |
|
~% 
5053-06-5 |
| Literature: Synthetic Communications, , vol. 24, # 10 p. 1483 - 1487 |
|
~% 
5053-06-5 |
| Literature: Chimica Therapeutica, , vol. 4, p. 185 - 194 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |