13761-79-0
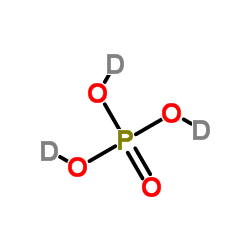
| Name | potassium,dideuterio phosphate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Potassium dideuterophosphate
deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate Potassium dideuterium phosphate MFCD00074894 EINECS 237-357-9 |
| Description | Phosphate monobasic-d2 (potassium) is the deuterium labeled Potassium phosphate monobasic[1]. Potassium phosphate monobasic (DiA) is a commonly used in biological assay buffers. Potassium phosphate monobasic is moderate to highly concentrated aqueous solutions of potassium phosphate monobasic for the production of phosphate buffers and other laboratory applications. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 158ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 253ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | D2KO4P |
| Molecular Weight | 138.09800 |
| Exact Mass | 137.94500 |
| PSA | 90.40000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.41mmHg at 25°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~% 
13761-79-0 |
| Literature: Lokshin Inorganic Materials, 1999 , vol. 35, # 7 p. 720 - 722 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |