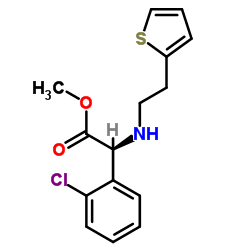
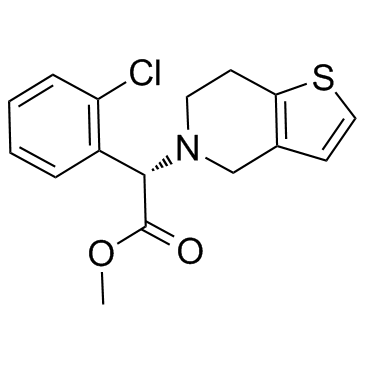
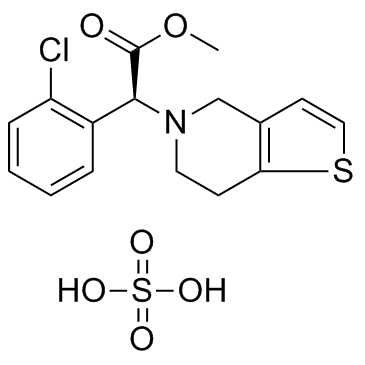
113665-84-2
| Name | clopidogrel |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(S)-Clopidogrel
Methyl-(2S)-(2-chlorphenyl)(6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)ethanoat thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H)-acetic acid, a-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydro-, methyl ester, (aS)- Plavix Clopilet Clopidogrelum (+)-Clopidogrel methyl (2S)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(6,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5-yl)acetate MFCD05662337 (S)-a-(2-Chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H)-acetic acid methyl ester Methyl (+)-(S)-a-(o-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H)-acetate Clopidogrel Methyl (2S)-(2-chlorophenyl)(6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)acetate Zyllt methyl (2S)-(2-chlorophenyl)(6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)ethanoate Thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H)-acetic acid, α-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydro-, methyl ester, (αS)- |
| Description | Clopidogrel is a well-known and orally active platelet inhibitor that targets P2Y12 receptor. Clopidogrel is used to inhibit blood clots in coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, and cerebrovascular disease. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
P2Y12 receptor[1]. |
| In Vivo | Clopidogrel, administered during the last three months, significantly decreases blood glucose, collagen and fibronectin expression compared to vehicle-treated diabetic mice. Clopidogrel markedly ameliorates hyperglycemia-induced renal fibrosis[1]. The combination therapy of clopidogrel and aspirin (dual-antiplatelet therapy) has been shown to be significantly beneficial compared to aspirin monotherapy and has also shown to decrease sub-acute stent thrombosis as well as recurrent ischemic events following ACS[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] 13-week-old C57BL/6J male mice are used throughout the study. After 1 week of acclimation, 15 mice are injected I.P. with streptozotocin (STZ) at a dosage of 55 mg/kg body weight daily for five consecutive days. Additional 15 mice as controls (Ctrl) are injected with a vehicle solution (0.1 mol/L citrate acid buffer, pH 4.3-4.5). Seven days after the last STZ administration, hyperglycemic mice (3-hour fasting blood glucose ≥250 mg/dL) are considered T1D (DM). This time point is defined as a baseline. Three months after diabetes induction, five diabetic and five control mice are sacrificed and blood and kidneys harvested. The remaining animals are divided in four groups: Normal control with vehicle (Ctrl), Normal control with Clopidogrel (Ctrl+ Clo), T1D (DM) with vehicle, and DM with Clopidogrel treatment (DM+Clo) and are treated with 20 mg/kg b.w./day Clopidogrel or with vehicle administered in their drinking water for three additional months. At the end of experiment, mice are intraperitoneally anesthetized with Avertin (tribromoethanol, 350 mg/kg) and sacrificed to collect blood and kidneys for mRNA, protein, and histological analyses[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 423.7±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C16H16ClNO2S |
| Molecular Weight | 321.822 |
| Flash Point | 210.0±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 321.059021 |
| PSA | 57.78000 |
| LogP | 4.23 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.617 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37-S22 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |

![4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/421/54903-50-3.png)