53866-34-5
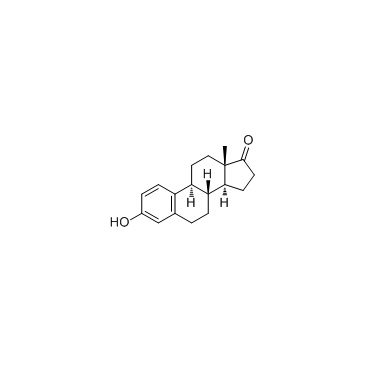
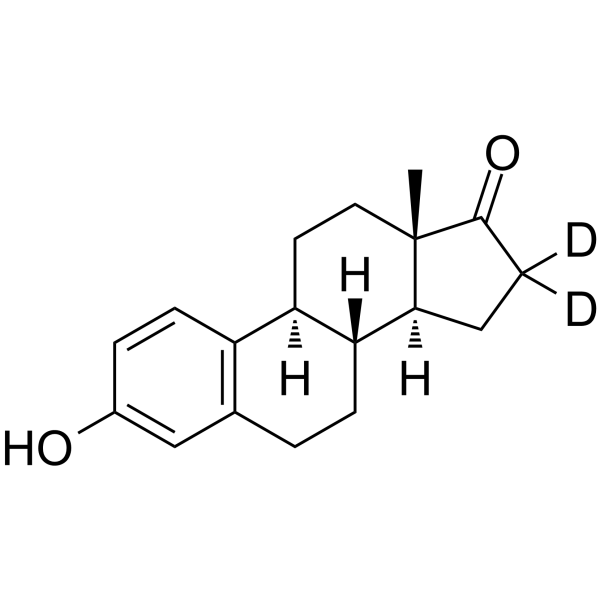
| Name | (8R,9S,13S,14S)-2,4,16,16-tetradeuterio-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Wynestron-d4
2,4,16,16-D4-estrone Estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one-2,4,16,16-d, 3-hydroxy- Cristallovar-d4 Crinovaryl-d4 Estrone-2,4,16,16-d4 Aquacrine-d4 Crystogen-d4 E1-2,4,16,16-d4 3-Hydroxy(2,4,16,16-H)estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one MFCD01074157 |
| Description | Estrone-d4 (E1-d4) is the deuterium labeled Estrone. Estrone (E1) is a natural estrogenic hormone. Estrone is the main representative of the endogenous estrogens and is produced by several tissues, especially adipose tissue. Estrone is the result of the process of aromatization of androstenedione that occurs in fat cells[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 445.2±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 258-260ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C18H18D4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 274.391 |
| Flash Point | 189.7±21.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 274.187073 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 3.69 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.587 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H350-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P308 + P313 |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Phrases | 60-61 |
| Safety Phrases | 53-22-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~95% 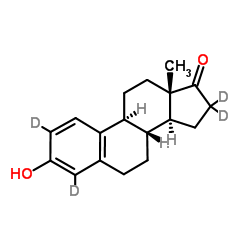
53866-34-5 |
| Literature: Kiuru, Paula S; Waehaelae, Kristiina Tetrahedron Letters, 2002 , vol. 43, # 18 p. 3411 - 3412 |
|
~% 
53866-34-5 |
| Literature: Steroids, , vol. 65, # 12 p. 883 - 888 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |