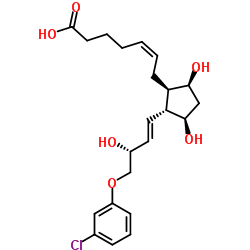
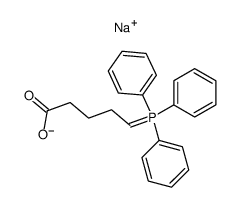
54276-21-0
| Name | (+)-Cloprostenol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5-Heptenoic acid, 7-((1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-((1E,3R)-4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxy-1-butenyl)-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl)-, (5Z)-rel-
5-Heptenoic acid, 7-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[(1E,3R)-4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxy-1-buten-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl]-, (5Z)- 5-Heptenoic acid, 7-((1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-((1E,3R)-4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxy-1-butenyl)-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl)-, monosodium salt, (5Z)-rel- (±)-Sodium (Z)-7-((1R*,2R*,3R*,5S*)-2-((E)-(3R*)-4-(m-Chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxy-1-butenyl)-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl)-5-heptenoate Cloprostenol Oestrophan Sodium (5Z)-7-{(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[(1E,3R)-4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxy-1-buten-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl}-5-heptenoate (Z)-7-[(1S,2S,3S,5R)-2-[(E,3S)-4-(3-chloranylphenoxy)-3-oxidanyl-but-1-enyl]-3,5-bis(oxidanyl)cyclopentyl]hept-5-enoic acid Dalmazin [veterinary] (TN) Racemic cloprostenol Estrophan (Z)-7-(2-((E)-4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxybut-1-enyl)-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl)hept-5-enoic acid (5Z)-rel-7-((1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-((1E,3R)-4-(3-Chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxy-1-butenyl)-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl)-5-heptenoic Acid Monosodium Salt (5Z)-7-{(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[(1E,3R)-4-(3-Chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxybut-1-en-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl}hept-5-enoic Acid Sodium (5Z)-7-{(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[(1E,3R)-4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxybut-1-en-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl}hept-5-enoate Cloprostenol Sodium 5-Heptenoic acid, 7-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[(1E,3R)-4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxy-1-buten-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl]-, sodium salt, (5Z)- (1:1) (5Z)-7-{(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[(1E,3R)-4-(3-Chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxy-1-buten-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl}-5-heptenoic acid Estrofan UNII:4208238832 Cloprostenol (INN) UNII:886SAV9675 (Z)-7-[(1S,2S,3S,5R)-2-[(E,3S)-4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-hydroxybut-1-enyl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl]-5-heptenoic acid |
| Description | (+)-Cloprostenol is a prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) analogue, and shows selective agonistic activity at the prostaglandin receptor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PGF2α |
| In Vitro | D-Cloprostenol and PGF2 alpha are equipotent, about 150 times more potent than dl-cloprostenol (P < 0.05) and approximately 280 times more potent than PGE1 in inhibiting [3H]PGF2 alpha binding to corpus luteum cell membranes. However, d-cloprostenol and PGF2 alpha are about 10 times more potent than dl-cloprostenol and approximately 95 times more potent than PGE1 in myometrial cell membranes[2]. |
| In Vivo | D-cloprostenol (15 g per head) is the lowest dose that consistently achieves abortion; D-cloprostenol causes mild adverse effects including salivation, defecation and hyperventilation in bitches weighing less than 10 kg. Intra-vesicle administration of a single low dose of d-cloprostenol is a safe and successful technique to induce abortion in the bitch[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 628.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C22H29ClO6 |
| Molecular Weight | 424.915 |
| Flash Point | 333.6±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 424.165253 |
| PSA | 110.05000 |
| LogP | 2.31 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.623 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
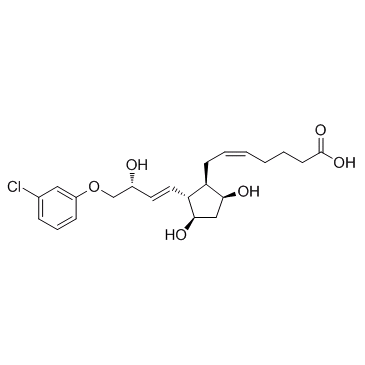
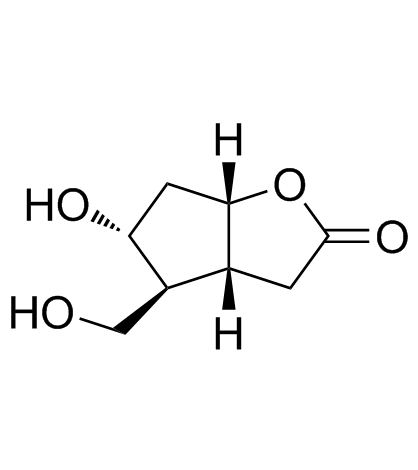
![4-[4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-3-oxobut-1-enyl]-5-hydroxy-3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydrocyclopenta[b]furan-2-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/284/53872-62-1.png)