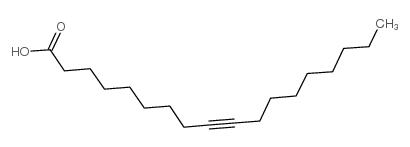
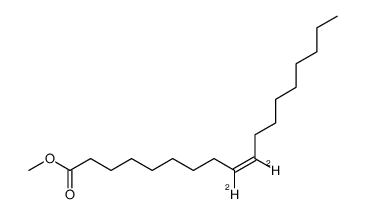
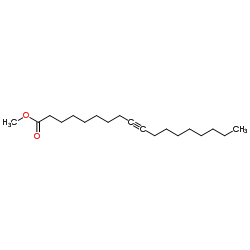
5711-29-5
| Name | oleic acid (9,10-d2) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
9,10-Dicyanoanthracen
<9,10-2H2>-oleic acid 9,10-anthracenedicarbonitrile 9,10-Dideutero-oelsaeure 9,10-Dideuterio-octadec-9c-ensaeure 9,10-dideuterio-octadec-9c-enoic acid 9,10-dideuterio-octadec-9-enoic acid 9,10-dicyanoanthracene |
| Description | Oleic acid-d2 (9-cis-Octadecenoic acid-d2) is the deuterium labeled Oleic acid. Oleic acid (9-cis-Octadecenoic acid) is an abundant monounsaturated fatty acid[1]. Oleic acid is a Na+/K+ ATPase activator[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.896 g/mL at 25ºC |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 192-195ºC/1.2 mmHg(lit.) |
| Melting Point | 13.4ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C18H32D2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 284.47400 |
| Exact Mass | 284.26800 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.10850 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
|
~87% 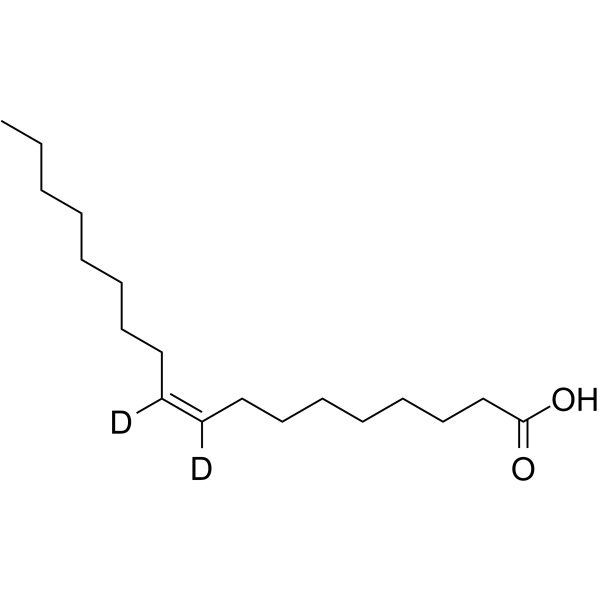
5711-29-5 |
| Literature: Haffner, Thomas; Tressl, Roland Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1996 , vol. 44, # 5 p. 1218 - 1223 |
|
~% 
5711-29-5 |
| Literature: Khan Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1952 , vol. 74, p. 3018,3021 |
|
~% 
5711-29-5 |
| Literature: Khan Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1952 , vol. 74, p. 3018,3021 |