286930-02-7
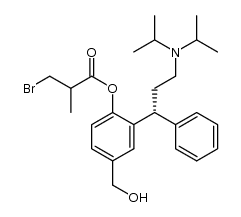
| Name | [2-[(1R)-3-[di(propan-2-yl)amino]-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl] 2-methylpropanoate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(R)-2-(3-N,N-diisopropylamino-1-phenylpropyl)-4-hydroxymethylphenoxyisobutyrate
(R)-(+)-isobutyric acid 2-[3-(diisopropylamino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl ester 2-methyl propanoic acid 2-[(1R)-3-[bis(1-methylethyl)amino]-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl) phenyl ester isobutyric acid 2-((R)-3-diisopropylanimonium-1-phenylpropyl)-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl ester (R)-Fesoterodine fumarate Fesoterodine (INN) FESO 2-[(1R)-3-(dipropan-2-ylamino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl 2-methylpropanoate |
| Description | Fesoterodine is an orally active, nonsubtype selective, competitive muscarinic receptor (mAChR) antagonist with pKi values of 8.0, 7.7, 7.4, 7.3, 7.5 for M1, M2, M3, M4, M5 receptors, respectively. Fesoterodine is used for the overactive bladder (OAB)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
pKi: 8.0 (M1), 7.7 (M2), 7.4 (M3), 7.3 (M4) and 7.5 (M5)[3] |
| In Vitro | Fesoterodine decreases micturition frequency, urgency severity and urgency incontinence episodes and increases the volume voided with each micturition[1]. After oral administration, Fesoterodine is rapidly and extensively hydrolysed in plasma by nonspecific esterases to Desfesoterodine (5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine; SPM 7605; HY-76569; an active metabolite of Fesoterodine)[3][4]. |
| In Vivo | Fesoterodine (0.01-1 mg/kg; IV) reduces the micturition pressure and increases bladder capacity and ICIs (intercontraction intervas) at the lowest dose tested of 0.01 mg/kg[3]. Animal Model: Bladders from female Sprague-Dawley rats (225-275 g)[3] Dosage: 0.01, 0.1 and 1 mg/kg Administration: IV Result: Reduced the micturition pressure and increased bladder capacity and ICIs at the lowest dose tested of 0.01 mg/kg. |
| References |
| Density | 1.043 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 518.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C26H37NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 412.58500 |
| Flash Point | 267.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 412.28500 |
| PSA | 49.77000 |
| LogP | 5.48800 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
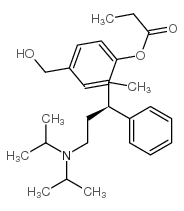
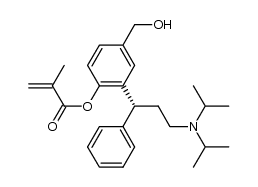
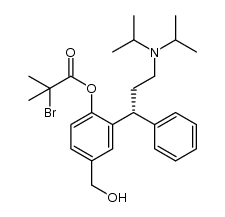



![3-[(1R)-3-[Bis(1-methylethyl)amino]-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(phenylmethoxy)-benzoic acid methyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/377/156755-35-0.png)