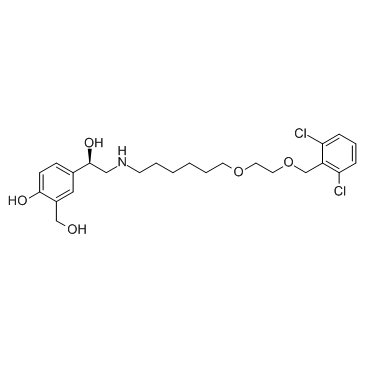
503068-34-6
| Name | vilanterol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Vilanterol
1,3-Benzenedimethanol, α-[[[6-[2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methoxy]ethoxy]hexyl]amino]methyl]-4-hydroxy-, (αR)- 4-{(1R)-2-[(6-{2-[(2,6-Dichlorobenzyl)oxy]ethoxy}hexyl)amino]-1-hydroxyethyl}-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol 4-[(1R)-2-[6-[2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methoxy]ethoxy]hexylamino]-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol |
| Description | Vilanterol is a long-acting β2-adrenoceptor (β2-AR) agonist with 24 h activity. The pEC50s for β2-AR,β1-AR and β3-AR is 10.37±0.05, 6.98±0.03 and 7.36±0.03, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
pEC50: 10.37±0.05 (β2-adrenoceptor), 6.98±0.03 (β1-adrenoceptor), 7.36±0.03 (β3-adrenoceptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | The selectivity of Vilanterol for β2-AR over the other β-AR receptor subtypes (β2 and β3) is established by testing the ability of Vilanterol to elicit concentration-dependent increases in cAMP in CHO cells expressing human β1-, β2-, and β3-AR. Vilanterol is demonstrated to be highly selective for the β2-AR with at least a 1000-fold selectivity over both β2- and β3-AR subtypes. This analysis results in a low-affinity pKD for [3H]Vilanterol of 9.44±0.07 (n=4) in the presence Gpp(NH)p and a high-affinity pKD of 10.82±0.12 (n=4) and a low-affinity pKD 9.47±0.17 (n=4) in the absence of Gpp(NH)p. In addition, a low-affinity pKD for [3H]Vilanterol of 9.52±0.24 (n=4) in the absence of Gpp(NH)p (37°C) is observed[1]. Vilanterol trifenatate is a novel inhaled long-acting β2-agonist with inherent 24 h activity in vitro in development as a combination with the inhaled corticosteroid fluticasone furoate for both COPD and asthma[2]. Vilanterol is a novel long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) with inherent 24-hour activity for once-daily clinical treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma in combination with the inhaled novel corticosteroid fluticasone furoate, also active for 24 hours[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Saturation, association, and dissociation binding studies are performed for [3H]Vilanterol to determine receptor binding kinetics at the β2-AR (equilibrium dissociation constant (KD), total number of receptors (Bmax), association rate (kon), and dissociation rate (koff) are calculated). For saturation binding, membranes (in a volume of 1.4 mL to avoid ligand depletion) are incubated with increasing concentrations of [3H]Vilanterol (~0.01-1.3 nM) for 5 h before filtration. For association binding, membranes are incubated with different concentrations of [3H]Vilanterol (~0.1-1.9 nM) for varying incubation times up to 1 h before filtration. For dissociation binding, membranes are preincubated for 1 h with a fixed concentration of [3H]Vilanterol (~1.1 nM) before dissociation is initiated by a 1:20 dilution in binding buffer (containing 10 μM cold Vilanterol) and then incubated for varying times up to 8 h before filtration. Saturation binding is also completed for [3H]CGP12177 (increasing concentrations of ~0.01-2.8 nM) in the same format as described above for [3H]Vilanterol. To determine the affinity of β2-AR agonists and antagonists, competition binding displacement studies are completed in which membranes are incubated with a fixed concentration of [3H]Vilanterol (~0.2 nM) and increasing concentrations of unlabeled agonist/antagonist for 5 h before filtration. All competition binding displacement studies are completed in the presence of 100 µM Gpp(NH)p to ensure that binding curves are monophasic[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 646.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C24H33Cl2NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 486.428 |
| Flash Point | 344.9±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 485.173584 |
| PSA | 91.18000 |
| LogP | 2.97 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.579 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |