162401-32-3
| Name | roflumilast |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Daxas
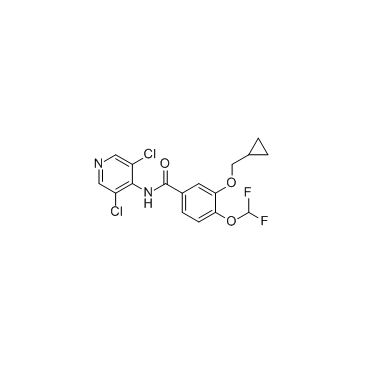
EINECS 223-583-8 3-(Cyclopropylmethoxy)-N-(3,5-dichloro-4-pyridinyl)-4-(difluoromethoxy)benzamide Benzamide, 3-(cyclopropylmethoxy)-N-(3,5-dichloro-4-pyridinyl)-4-(difluoromethoxy)- MFCD00938270 Roflumilast 3-(CYCLOPROPYLMETHOXY)-N-(3,5-DICHLOROPYRIDIN-4-YL)-4-(DIFLUOROMETHOXY)BENZAMIDE Daliresp |
| Description | Roflumilast is a selective PDE4 inhibitor with IC50s of 0.7, 0.9, 0.7, and 0.2 nM for PDE4A1, PDEA4, PDEB1, and PDEB2, respectively, without affecting PDE1, PDE2, PDE3 or PDE5 isoenzymes from various cells. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.7 nM (PDE4A1), 0.9 nM (PDE4A4), 0.7 nM (PDE4B1), 0.2 nM (PDE4B2)[1] |
| In Vitro | Roflumilast does not affect PDE enzymes apart from PDE4, and is a subnanomolar inhibitor of most PDE4 splicing variants tested. It showed no PDE4 subtype selectivity apart from PDE4C (4C1, IC50=3 nM; 4C2, IC50=4.3 nM), which is inhibited with a slightly lower potency[2]. Roflumilast is a potent and selective PDE4 inhibitor. Roflumilast is a monoselective PDE4 inhibitor since it does not affect other PDE isoenzymes, including PDE1, PDE2, PDE3, and PDE5 up to 10,000-fold higher concentrations. Roflumilast inhibits human neutrophil functions. Roflumilast inhibits TNFα synthesis in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Rolfumilast inhibits proliferation and cytokine synthesis in CD4+ T cells. Proliferation is inhibited to a maximum of about 60% by Roflumilast with a potency (IC30) of 7 nM[3]. |
| In Vivo | Animal studies with Roflumilast demonstrated that it reduced the accumulation of neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid following short-term exposure of guinea pigs, mice or rats to tobacco smoke, and following exposure of rats to a combination of tobacco smoke and bacterial lipopolysaccharide, and abolished the lung parenchymal influx of inflammatory cells seen in rats exposed to tobacco smoke for 7 months[2]. Roflumilast blocks COPD progression in pIgR−/− mice. For these studies, 9-month-old WT or pIgR−/− mice are treated daily by oral gavage with 100 μg of Roflumilast (5 μg/g) or vehicle (4% methylcellulose, 1.3% PEG400) for 3 months and lungs are harvested at 12 months of age. Unlike pIgR−/− mice treated with vehicle, mice treated with Roflumilast had no progression of small airway wall remodelling after starting treatment. Strikingly, 12-month-old pIgR−/− mice treated with Roflumilast had reduced indices of emphysema compared with 9-month-old pIgR−/− mice, indicating that Roflumilast not only blocks progression of emphysema in this model but apparently facilitates some resolution of the emphysematous destruction of lung parenchyma[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | PDE activity is determined with some modifications. The assay mixture contain 50 mM Tris (pH 7.4), 5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 μM cAMP or cGMP, and [3H]cAMP or [3H]cGMP (about 30,000 cpm/assay), the indicated concentration of the inhibitor and an aliquot of the enzyme solution at a final assay volume of 200 μL. Stock solutions of the compounds are diluted 1:100 (v/v) in the Tris buffer mentioned above; appropriate dilutions are prepared in 1% (v/v) DMSO/Tris buffer, which are diluted 1:2 (v/v) in the assays to obtain the desired final concentrations of the inhibitors at a DMSO concentration of 0.5% (v/v). DMSO itself affected none of the PDE activities. After preincubation for 5 min at 37°C, the reaction is started by the addition of substrate (cAMP or cGMP) and the assays are incubated for further 15 min at 37°C. Then 50 μL of 0.2 N HCl is added to stop the reaction and the assays are left on ice for about 10 min. Following incubation with 25 μg of 5′-nucleotidase (Crotalus atrox snake venom) for 10 min at 37°C, the assays are loaded on QAE Sephadex A-25 (1 mL of bed volume in Poly-Prep chromatography columns). The columns are eluted with 2 mL of 30 mM ammonium formate (pH 6.0) and the eluate is counted for radioactivity. Results are corrected for blank values (measured in the presence of denatured protein) that are below 5% of total radioactivity. The amount of cyclic nucleotides hydrolyzed did not exceed 30% of the original substrate concentration[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[4] WT or pIgR−/− mice are used. For studies using Roflumilast, 200 μL of 0.5 mg/mL suspension of Roflumilast or vehicle (4% methylcellulose, 1.3% PEG400 and 5 μg drug per mg animal weight) is administered by oral gavage once daily, 5 days a week for the duration of treatment. Mice are treated daily by oral gavage with 100 μg of Roflumilast (5 μg/g) or vehicle (4% methylcellulose, 1.3% PEG400) for 3 months and lungs are harvested at 12 months of age. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 430.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 158°C |
| Molecular Formula | C17H14Cl2F2N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 403.207 |
| Flash Point | 214.2±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 402.034943 |
| PSA | 60.45000 |
| LogP | 4.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.604 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |