| Description |
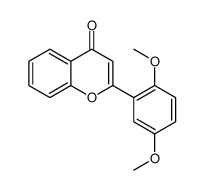
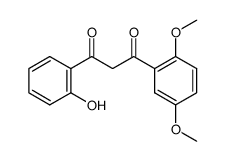
6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone is a novel antagonist of GABAA receptor.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
GABAA receptor[1]
|
| In Vitro |
6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone is a novel antagonist of GABAA receptor. 6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone inhibits [3H]-flunitrazepam binding to the rat cerebral cortex membranes with a Ki of 37.2±4.5 nM. The current elicited with the EC50 concentration of GABA is decreased to 73.6±1.9% of control by co-application of 5 μM 6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone (n=5), compare to a decrease to 65.9±3.0% by 1 μM FG-7142 (n=5). The EC50 for GABA dose response increases from 47.6 to 59.7 μM upon co-application of 5 μM 6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone, and the maximal GABA-current is decreased[1].
|
| In Vivo |
6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone-treated mice exhibit significant differences from control mice with respect to the percentage of open arms entries [F(4,73)=8.01, P<0.0001] and the percentage of time spent in open arms [F (4,73)=5.19, P<0.002], but not the number of entries to closed arms [F(4,73)= 0.79,P=0.54]. The post-hoc NewmaneKeuls’ tests confirm that 6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone significantly decreases the percentage of open arm entries and time spent in open arms at the doses of 8 and 16 mg/kg. 6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone treatment similarly increases step-through latency [F(4,75)=4.71, P<0.002], suggesting enhanced cognitive performance[1].
|
| Cell Assay |
Membranes from HEK 293T cell are used in this study. Briefly, aliquots of membranes are incubated with 1 nM [3H]-flunitrazepam or 8 nM [3H]-Ro15-4513 at 4°C for 90 min in the presence or absence of 6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone. After incubation, the mixtures are filtered onto Whatman GF/B filters with a Brandel 24-well harvester. Each filter is incubated for at least 1 h with 4 mL scintillation cocktail before measurement of radioactivity in a Beckman-Coulter LS 6500 scintillation counter. For saturation analysis, the membranes are incubated with increasing concentrations of [3H]-flunitrazepam or [3H]-Ro15-4513. Binding affinity is determined by nonlinear regression analysis[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Male ICR mice are randomized into six groups (n=12 to 16/group), and receive 0.4 mg/kg scopolamine (i.p.) 45 min prior to training, followed with vehicle (dd water, pH 9.0, p.o.), 2, 4, 8 or 16 mg/kg 6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone (p.o.), or 30 mg/kg FG-7142 (i.p.) 30 min prior to training. On the training trials, each mouse is placed into the lighted chamber of a two-compartment box, and the door leading to the dark chamber is opened 10 s later. Once the mouse enters the dark compartment, the door is closed and an inescapable electric foot-shock (0.4 mA, 1 s) is delivered from the grid floor. The mouse is removed from the apparatus 10 s later. The step-through latency is recorded, with the cut-off step-through latency set at 300 s[1].
|
| References |
[1]. Wang F, et al. 6,2'-Dihydroxyflavone, a subtype-selective partial inverse agonist of GABAA receptor benzodiazepine site. Neuropharmacology. 2007 Sep;53(4):574-82.
|