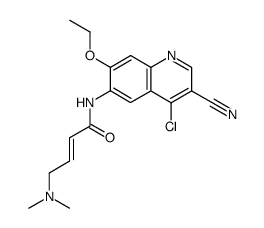
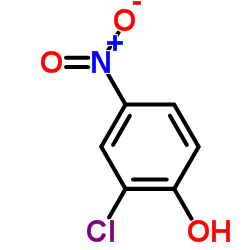
698387-09-6
| Name | neratinib |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
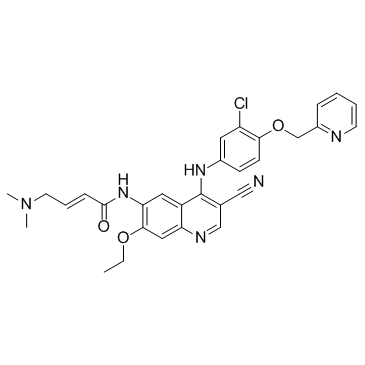
(2E)-N-[4-[[3-chloro-4-[(pyridin-2-yl)methoxy]phenyl]amino]-3-cyano-7-ethoxyquinolin-6-yl]-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide
HKI 272 (E)-N-[4-[3-chloro-4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)anilino]-3-cyano-7-ethoxyquinolin-6-yl]-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide (E)-N-{4-[3-chloro-4-(2-pyridinylmethoxy)anilino]-3-cyano-7-ethoxy-6-quinolinyl}-4-(dimethylamino)-2-butenamide free base S2150_Selleck N-(4-(3-chloro-4-(2-pyridinylmethoxy)anilino)-3-cyano-7-ethoxy-6-quinolyl)-4-(dimethylamino)-2-butenamide (2E)-N-(4-{[3-Chloro-4-(2-pyridinylmethoxy)phenyl]amino}-3-cyano-7-ethoxy-6-quinolinyl)-4-(dimethylamino)-2-butenamide (E)-N-(4-(3-chloro-4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)phenylamino)-3-cyano-7-ethoxyquinolin-6-yl)-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide Neratinib(HKI-272) (E)-N-{4-[3-chloro-4-(2-pyridinylmethoxy)anilino]-3-cyano-7-ethoxy-6-quinolinyl}-4-(dimethylamino)-2-butenamide (2E)-N-(4-{[3-chloro-4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)phenyl]amino}-3-cyano-7-ethoxyquinolin-6-yl)-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide [2H]-Neratinib 2-Butenamide, N-[4-[[3-chloro-4-(2-pyridinylmethoxy)phenyl]amino]-3-cyano-7-ethoxy-6-quinolinyl]-4-(dimethylamino)-, (2E)- Neratinib |
| Description | Neratinib is an orally available, irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50s of 59 nM and 92 nM for HER2 and EGFR, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EGFR:92 nM (IC50) HER2:59 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Neratinib has inhibition of tyrosine kinases KDR and Src with IC50 of 0.8 μM and 1.4 μM, respectively, being 14- and 24-fold less active compared with HER2. Neratinib displays no activity against other serine-threonine kinases such as Akt, cyclin D1/cdk4, cyclin E/cdk2, cyclin B1/cdk1, IKK-2, MK-2, PDK1, c-Raf, and Tpl-2, as well as the tyrosine kinase c-Met. Neratinib selectively inhibits the proliferation of 3T3 cells transfected with the HER2 (3T3/neu), as well as two other HER-2-overexpressing SK-Br-3 and BT474 cells with IC50 values of 2-3 nM, displaying > 230-fold potency compared with non-transfected 3T3 cells as well as MDA-MB-435 and SW620 which are EGFR- and HER2-negative. Neratinib also inhibits the proliferation of EGFR-dependent A431 cells with an IC50 of 81 nM. Neratinib reduces HER2 receptor autophosphorylation in BT474 cells with an IC50 of 5 nM, and EGF-dependent phosphorylation of EGFR in A431 cells with IC50 of 3 nM. Blocking of HER-2 by Neratinib results in inhibition of downstream MAPK and Akt pathways with IC50 of 2 nM, more potently than Trastuzumab. Neratinib inhibits the cyclin D1 expression and the phosphorylation of the Rb-susceptibility gene production in BT474 cells with IC50 of 9 nM, leading to G1-S arrest and ultimately decreased cell proliferation[1]. |
| In Vivo | Orally treated neratinib significantly inhibits the growth of 3T3/neu xenografts, with inhibition of 34%, 53%, 98%, and 98% at dose of 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg/day, respectively. Consistent with the inhibition of HER-2 phosphorylation by 84% within 1 hour of administration at 40 mg/kg/day, Neratinib inhibits the growth of BT474 xenografts by 70-82%, 67%, and 93% at dose of 5, 10, and 40 mg/kg/day, respectively. Neratinib is also effective against SK-OV-3 xenografts with inhibition of 31% and 85% at 5 and 60 mg/kg/day, respectively. Neratinib is less potent against EGFR-dependent A431 xenografts than HER-2-dependent tumors, with 32% and 44% inhibition at 5 and 20 mg/kg/day, respectively. Neratinib displays little activity against MCF-7 and MX-1 xenografts expressing low levels of HER-2 and EGFR, with only 28% inhibition at 80 mg/kg/day, suggesting that Neratinib has selective activity for cells expressing HER-2 or EGFR[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Neratinib is prepared as 10 mg/mL stocks in DMSO and diluted in 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.5; 0.002 ng/mL-20 μg/mL). Purified recombinant COOH-terminal fragments of HER2 (amino acids 676-1255) or epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) (amino acids 645-1186) [diluted in 100 mM HEPES (pH 7.5) and 50% glycerol] is incubated with increasing concentrations of Neratinib in 4 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.4 mM MnCl2, 20 μM sodium vanadate, and 0.2 mM DTT for 15 minutes at room temperature in 96-well ELISA plates. The kinase reaction is initiated by the addition of 40 μM ATP and 20 mM MgCl2 and allowed to proceed for 1 hour at room temperature. Plates are washed, and phosphorylation is detected using Europium-labeled anti-phospho-tyrosine antibodies (15 ng/well). After washing and enhancement steps, signal is detected using a Victor2 fluorescence reader (excitation wavelength 340 nm, emission wavelength 615 nm). The concentration of Neratinib that inhibits receptor phosphorylation by 50% (IC50) is calculated from inhibition curves. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are exposed to various concentrations of Neratinib for 2, or 6 days. Cell proliferation is determined using sulforhodamine B, a protein binding dye. Briefly, cells are fixed with 10% trichloroacetic acid and washed extensively with water. Cells are then stained with 0.1% sulforhodamine B and washed in 5% acetic acid. Protein-associated dye is solubilized in 10 mM Tris, and absorbance is measured at 450 nM. The concentration of Neratinib that inhibits cell proliferation by 50% (IC50) is determined from inhibition curves. |
| Animal Admin | Tumor cells (maintained in tissue culture) or tumor fragments are implanted s.c. in the flanks of female athymic (nude) mice. For estrogen-dependent cell lines (BT474, MCF-7, and SK-OV-3), animals are implanted with hormone pellets (0.72 mg of 17-β estradiol, 60-day release) 1 week before implantation of tumors. Additionally, SK-OV-3 cells are suspended in Matrigel basement membrane matrix for implantation. Treatment is initiated after tumors hads reached a size of 90-200 mg, following random assignment of the animals to different treatment groups (staging, day 0). For 3T3/neu xenografts, treatment is initiated the day after tumor implantation (day 0). HKI-272 is formulated in 0.5% methocellulose-0.4% polysorbate-80 (Tween 80) and administered daily, p.o., by gavage. Tumor mass [(length × width2)/2] is determined every 7 days. Tumor outgrowth in all xenograft studies, except 3T3/neu, is expressed as relative tumor growth: the ratio of the mean tumor mass to the mean tumor mass on day 0. Inhibition of tumor growth is calculated relative to vehicle-treated controls. Statistical significance of inhibition is demonstrated using one-tailed Student’s t test (equal variance) after log transformation of the data. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 757.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 184 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C30H29ClN6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 557.043 |
| Flash Point | 411.6±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 556.198975 |
| PSA | 112.40000 |
| LogP | 5.46 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.667 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 29334900 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
![6-amino-4-[3-chloro-4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)anilino]-7-ethoxyquinoline-3-carbonitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/300/848139-78-6.png)
![3-Chloro-4-[(pyridin-2-yl)methyloxy]aniline structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/030/524955-09-7.png)