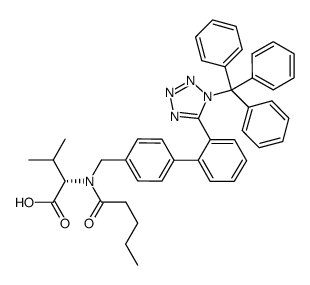
137862-53-4
| Name | valsartan |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Valsartan
(S)-N-(1-Carboxy-2-methylprop-1-yl)-N-pentanoyl-N-[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]amine N-Pentanoyl-N-{[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-L-valine N-Pentanoyl-N-{[2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-L-valine N-Pentanoyl-N-{[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-L-valine N-Valeryl-N-[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]-L-valine N-Pentanoyl-N-{[2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}valine N-(1-Oxopentyl)-N-[[2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-L-valine (2S)-3-Methyl-2-(pentanoyl{[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}amino)butanoic acid N-[p-(o-1H-Tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]-N-valeryl-L-valine 3-Methyl-2-[pentanoyl-[[4-[2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]amino]-butanoic acid Nisis N-Pentanoyl-N-{[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-L-valin (2S)-3-Methyl-2-(pentanoyl{[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}amino)butanoic acid Valsratan N-(1-Oxopentyl)-N-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-L-valine Valine, N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]- Tareg DIOVAN L-Valine, N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]- Valsartane Valsartan API (S)-2-(N-((2'-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)pentanamido)-3-methylbutanoic acid L-Valsartan MFCD00865840 |
| Description | Valsartan (CGP-48933) is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist for treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Valsartan is a synthetic non-peptide angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist that dilates blood vessels and reduces blood pressure by blocking the action of angiotensin. Valsartan significantly decreases the expression of AT1R in ageing aorta endothelial cells[1]. The pretreatment of valsartan results in an inhibition of TLR2 signaling and proinflammatory cytokines. The expression of AGTR1 is up-regulated after alcohol exposure, and is blocked by valsartan pretreatment[2]. |
| In Vivo | Valsartan significantly attenuates the expression of TGF-β/Smad, Hif-1α and fibrosis-related protein in rats after MI. Heart function, infarcted size, wall thickness as well as myocardial vascularization of ischaemic hearts are also significantly improved by valsartan compared with saline and hydralazine[3]. Valsartan partially reverses the effects of high-salt diet on hypertension, cardiac injuries such as fibrosis and inflammatory cell infiltration, and inhibition of aquaporin 1 and angiogenic factors; valsartan alone does not exert such effects[4]. Valsartan is an effective antidepressant/antianxiety reagent and can promote the hippocampal neurogenesis and expression of BDNF. Chronic administration of valsartan (5-40 mg/kg/d, p.o.) increases the time spent in the center of the field in OFT and the latency to eat in NSF, reduces the immobility time in both TST and FST, and increases the sucrose preference in SPT[5]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Rats are randomly divided into two groups: (i) valsartan-treated group that is given intravenously 3 mg/kg/day valsartan in 0.5 mL normal saline via the vein daily for 1 week; (ii) hydralazine-treated group receiving 0.2 mg/kg/day hydralazine injection in saline; and (iii) control group that receives saline injection in the same way (n=15 for each group)[4]. Mice: Valsartan is dissolved in water containing 0.5% methylcellulose solution. Valsartan (5-40 mg/kg/d) is administered by oral (p.o.) route in a volume of 10 mL/kg body weight using the gavage technique. Potential alteration in blood pressure in response to chronic treatment with valsartan is assessed with a commercial blood pressure analysis systemdesigned. The mice are trained for at least 2 consecutive days to adapt to the apparatus before the study is initiated. To record the blood pressure, the mice are placed on a heated pad (35°C) and measured with a programmable tail-cuff sphygmomanometer in steady state. The average of 10 readings from each mouse is recorded[5]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 684.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 116-117°C |
| Molecular Formula | C24H29N5O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 435.519 |
| Flash Point | 368.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 435.227051 |
| PSA | 112.07000 |
| LogP | 4.75 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.587 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| Stability | Hygroscopic |
| Hazard Statements | H413 |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |

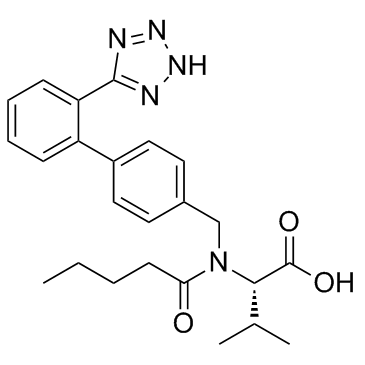
![N-[(2'-(1-triphenylmethyl-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-N-valeroyl-(L)-valine benzyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/128/137864-44-9.png)
![(S)-4-isopropyl-3-pentanoyl-2-[2'-(2-trityl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-yl]oxazolidin-5-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/129/852212-82-9.png)
![(2S)-3-methyl-2-{N-[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]-N'-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-amino}-butanoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/168/1033772-60-9.png)
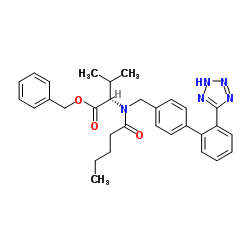

![(S)-METHYL 3-METHYL-2-(N-((2'-(1-TRITYL-1H-TETRAZOL-5-YL)-[1,1'-BIPHENYL]-4-YL)METHYL)PENTANAMIDO)BUTANOATE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/126/781664-81-1.png)
![N-[(2'-Cyano[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl]-N-(1-oxopentyl)-L-valine methyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/081/137863-90-2.png)