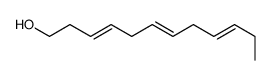
2566-90-7
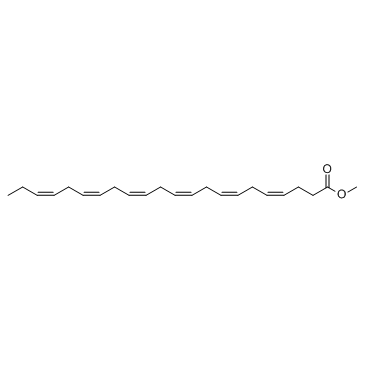
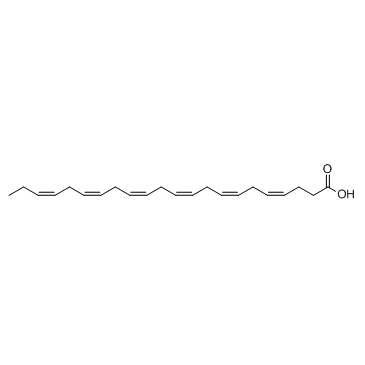
| Name | Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid, methyl ester, (all-Z)-
fame 22:6n-3 docosa-4c,7c,10c,13c,16c,19c-hexaenoic acid methyl ester all-cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid methyl ester Methyl (4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoate 4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid, methyl ester, (4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)- Methyl (4E,7E,10E,13E,16E,19E)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoate Methyl (4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoate DHA methyl ester Docosahexaenoic acid methyl Docosa-4c,7c,10c,13c,16c,19c-hexaensaeure-methylester methyl 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoate 4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid, methyl ester, (4E,7E,10E,13E,16E,19E)- all-cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid methyl ester solution Fame 22:6n-3,Methyl all-cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexenoate,Methyl DHA |
| Description | Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester is a methylated docosahexaenoic acid analog which can be intercalated into membrane phospholipids without being oxidized or hydrolyzed. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Sharp wave (SPW) incidence relative to baseline appears to decrease following Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester (DHA-Me) application[1]. There is no generation of a new protein band when bovine serum albumin (BSA) is exposed to the Fe2+ and ascorbic acid (AsA) mixed-function oxidation system in the absence of Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester (DHA). However, the high-molecular-weight protein band is observed after only 24 h when BSA is incubated with DHA. Incubation of BSA with 1.0 mM DHA leads to a substantial increase in protein carbonyl content and the addition of oxygen radical scavengers leads to a substantial decrease in protein carbonyl content[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Protein (1 mg/mL) is incubated with Docosahexaenoic Acid methyl ester (DHA) (1.0 mM) in 50 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) containing 0.2% (w/v) of Tween 20 at 37°C. Mannitol, histidine, sodium benzoate, or KI is added at final concentration of 0.5 M, 0.2 M, 0.5 M, or 0.1 M, respectively. Reactive oxygen species are generated by addition of FeSO4 (1 μM) and ascorbic acid (AsA, 20 μM)[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 429.9±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C23H34O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 342.515 |
| Flash Point | 103.9±21.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 342.255890 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 7.24 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.505 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;half-mask respirator (US);multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | F,N,Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 11-67-65-50/53-38 |
| Safety Phrases | 16-62-61-24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN1170 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Hazard Class | 3.0 |
| HS Code | 29161900 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |