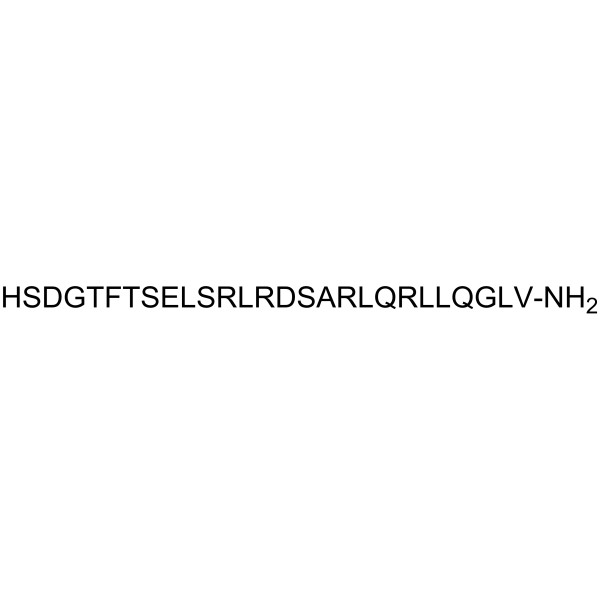| Description |
Secretin (swine), a neuroendocrine hormone, is the first hormone to be identifie and is secreted by S cells that are localized primarily in the mucosa of the duodenum. Secretin also is a 27-amino acid peptide, which acts on secretin receptors. Secretin is expressed by cells in all mature enteroendocrine cell subsets and can be prompted by fatty acids. Secretin stimulates the secretion of pancreatic water and bicarbonate. Secretin exerts various effects in organs, can be used for the research of digestive system, central nervous system and energy metabolism[1][2].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| In Vitro |
Secretin (swine) (10−7M, 10−6M; 24 to 72 h and 7 days) stimulates biliary growth by interaction with secretin receptors (SR) and knockout of SR reduces biliary proliferation by downregulating cAMP dependent signaling[2]. Secretin (10−7M, 10−6M; 24 to 72 h and 7 days) increases the proliferation in human HIBEpiC and large murine cholangiocyte lines[2][3][4]. Immunofluorescence[2] Cell Line: large murine cholangiocyte lines Concentration: 10−7M, 10−6 M Incubation Time: 24 to 72 h and 7 days Result: Increased the proliferation of cholangiocytes. Cell Proliferation Assay[2] Cell Line: human HIBEpiC and large murine cholangiocyte lines Concentration: 10−7M, 10−6M Incubation Time: 24 to 72 h and 7 days Result: Increased the proliferation of non-transfected, vector-transfected and secretin shRNA large cholangiocytes and HiBEpiC compared to the cell lines treated with BSA (basal).
|
| In Vivo |
Secretin (swine) (2.5 nM/kg, BW/day, osmotic minipumps, for 1 week) stimulates biliary cell proliferation by regulating expression of microRNA 125b and microRNA let7a in mice[2]. Animal Model: Sct+/-mice[2] Dosage: 2.5 nM/kg Administration: 2.5 nM/kg, BW/day, osmotic minipumps, for 1 week Result: Increased in supernatants from cholangiocytes and S cells and in serum and bile following BDL in control mice. Had low IBDM, reduced proliferation, and reduced production of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and nerve growth factor (NGF) in BDL Sct+/-mice. Regulated VEGF and NGF expression that negatively correlated with microRNA 125b and let7a levels in liver tissue[2].
|
| References |
[1]. Katharina Schnabl, et al. Secretin as a Satiation Whisperer With the Potential to Turn into an Obesity-curbing Knight. Endocrinology. 2021 Sep 1;162(9):bqab113. [2]. Shannon Glaser, et al. Secretin stimulates biliary cell proliferation by regulating expression of microRNA 125b and microRNA let7a in mice. Gastroenterology. 2014 Jun;146(7):1795-808.e12. [3]. G Alpini, et al. Morphological, molecular, and functional heterogeneity of cholangiocytes from normal rat liver. Gastroenterology. 1996 May;110(5):1636-43. [4]. Shannon Glaser, et al. Knockout of secretin receptor reduces large cholangiocyte hyperplasia in mice with extrahepatic cholestasis induced by bile duct ligation. Hepatology. 2010 Jul;52(1):204-14.
|