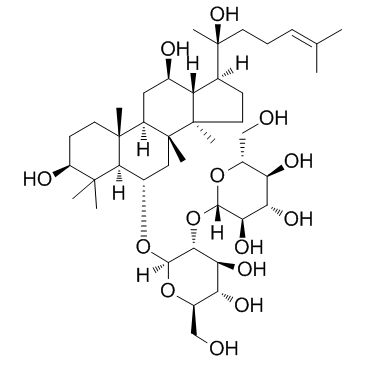
52286-58-5
| Name | ginsenoside Rf |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(3β,6α,12β)-3,12,20-Trihydroxydammar-24-en-6-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
Ginsenoside Rf GinsenosideRf β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,6α,12β)-3,12,20-trihydroxydammar-24-en-6-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl- PANAXOSIDE RF ginsinoside Rf |
| Description | Ginsenoside Rf is a trace component of ginseng root. Ginsenoside Rf inhibits N-type Ca2+ channel. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
N-Type Ca2+ Channel |
| In Vitro | Ginsenoside Rf is a saponin, which is present in only trace amounts within ginseng. At saturating concentrations, Ginsenoside Rf rapidly and reversibly inhibits N-type, and other high-threshold, Ca2+ channels in rat sensory neurons to the same degree as a maximal dose of opioids. The effect is dose-dependent (half-maximal inhibition: 40 μM) and it is virtually eliminated by pretreatment of the neurons with pertussis toxin, an inhibitor of G(o) and Gi GTP-binding proteins. Ginsenoside Rf also inhibits Ca2+ channels in the hybrid F-11 cell line[1]. |
| In Vivo | Since inhibition of Ca2+ channels in sensory neurons contributes to antinociception by opioids, analgesic actions of Ginsenoside Rf are tested. Dose-dependent antinociception is found by systemic administration of Ginsenoside Rf in mice using two separate assays of tonic pain: in the acetic acid abdominal constriction test, the ED50 is 56±9 mg/kg, a concentration similar to those reported for aspirin and acetaminophen in the same assay; in the tonic phase of the biphasic formalin test, the ED50 is 129±32 mg/kg[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Naive, adult (7-12 week old) mice of outbred Swiss-Webster stock are used in all in vivo experiments. Mice are brought to a quiet testing room, and acclimated to table-top Plexiglas observation chambers (30 cm high; 30 cm diameter) for 30 min. They are then weighed and injected with Ginsenoside Rf (25, 50, or 75 mg/kg) or vehicle (preceded by naloxone or saline in one experiment). Twenty min later, a 0.9% solution of glacial acetic acid is injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) in a volume of 10 mL/kg. For the next 30 min, the number of constrictions (writhes)-strong contractions of the abdominal musculature accompanied by dorsoflexion of the back and extension of the hindlimbs-are counted and recorded in 5-min blocks. Four mice (one per chamber) are observed simultaneously by a single, experienced experimenter. To control for the considerable circadian and other environmental variance accompanying this nociceptive assay, two vehicle controls are tested alongside two Ginsenoside Rf-administered mice in every experimental session[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 912.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C42H72O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 801.013 |
| Flash Point | 505.5±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 800.492188 |
| PSA | 239.22000 |
| LogP | 3.51 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.602 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22 |
| Safety Phrases | 2-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | LY9536900 |
| HS Code | 29389090 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |