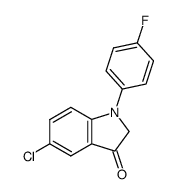
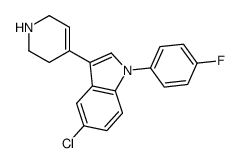
106516-24-9
| Name | sertindole |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
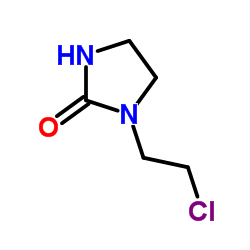
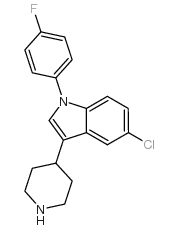
1-[2-[4-[5-chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)indol-3-yl]piperidin-1-yl]ethyl]imidazolidin-2-one
1-(2-{4-[5-Chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-1-piperidinyl}ethyl)-2-imidazolidinone 1-[2-[4-[5-chloro-1-(p-fluorophenyl)indol-3-yl]piperidino]ethyl]-2-imidazolidinone 1-[2-[4-[5-chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1h-indol-3-yl]-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-2-imidazolidinone 2-Imidazolidinone, 1-[2-[4-[5-chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]- 2-Imidazolidinone, 1-[2-[4-[5-chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-1-piperidinyl]ethyl] 1-(2-{4-[5-Chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]piperidin-1-yl}ethyl)imidazolidin-2-one MFCD00867749 Sertindole |
| Description | Sertindole, a neuroleptic, is one of the newer antipsychotic medications available.Target: Multi-targetIn vitro studies showed that sertindole exerts a potent antagonism at serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, dopamine D2, and αl adrenergic receptors. Sertindole offers an alternative treatment option for refractory patients given its good EPS profile, favorable metabolic profile, and comparable efficacy to risperidone. Due to cardiovascular safety concerns, sertindole is available as a second-line choice for patients intolerant to other antipsychotic agents [1]. Sertindole should prove to be a very useful addition to the therapeutic options available for the treatment of psychotic disorders [2]. Sertindole improves negative symptoms, and is also effective for the treatment of neuroleptic-resistant schizophrenia. Sertindole is generally well tolerated and is associated with a low rate of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Thus, sertindole is a useful option in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 592.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 95-100ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C24H26ClFN4O |
| Molecular Weight | 440.941 |
| Flash Point | 311.9±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 440.177917 |
| PSA | 40.51000 |
| LogP | 5.26 |
| Appearance | off-white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.671 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: >10mg/mL |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335-H413 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | NJ0621100 |
|
~87% 
106516-24-9 |
| Literature: Perregaard; Arnt; Bogeso; Hyttel; Sanchez Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1992 , vol. 35, # 6 p. 1092 - 1101 |
|
~% 
106516-24-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 6 p. 1092 - 1101 |
|
~% 
106516-24-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 6 p. 1092 - 1101 |
|
~% 
106516-24-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 6 p. 1092 - 1101 |
|
~% 
106516-24-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 6 p. 1092 - 1101 |
|
~% 
106516-24-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 6 p. 1092 - 1101 |
|
~% 
106516-24-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 35, # 6 p. 1092 - 1101 |
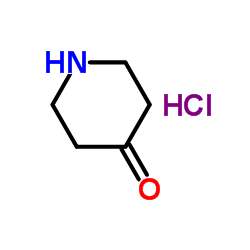
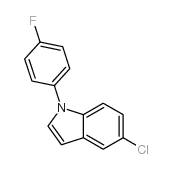
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |