936350-00-4
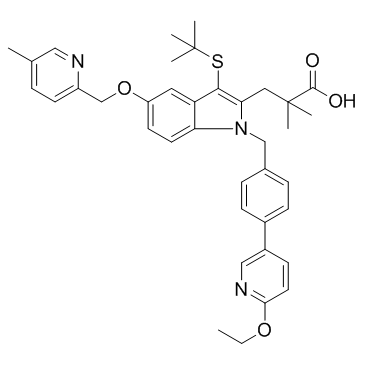
| Name | 3-[3-tert-butylsulfanyl-1-[[4-(6-ethoxypyridin-3-yl)phenyl]methyl]-5-[(5-methylpyridin-2-yl)methoxy]indol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
FIBOFLAPON
AM 803 Fiboflapon (USAN) UNII-Y1NA96IX3T Fiboflapon [USAN:INN] GSK2190915 |
| Description | Fiboflapon (GSK2190915) is a potent FLAP(5-Lipoxygenase-activating protein) inhibitor with binding IC50 of 2.9 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 76 nM (inhibition of LTB4 in human blood 5 h incubation)[1]. |
| In Vitro | Fiboflapon (AM-803) exhibits excellent preclinical toxicology and pharmacokinetics in rat and dog. Fiboflapon (AM-803) also demonstrated an extended pharmacodynamic effect in a rodent bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) model [1]. |
| In Vivo | Oral administration of Fiboflapon (AM-803: 1 mg/kg) results in sustained inhibition of ex vivo ionophore-challenged whole blood LTB4 biosynthesis with >90% inhibition for up to 12 h and an EC50 of approximately 7 nM. When rat lungs are challenged in vivo with calcium-ionophore, Fiboflapon (AM-803) inhibits LTB4 and cysteinyl leukotriene (CysLT) production with ED50s of 0.12 mg/kg and 0.37 mg/kg, respectively. The inhibition measured 16 h following a single oral dose of 3 mg/kg was 86% and 41% for LTB4 and CysLTs, respectively. In an acute inflammation setting, Fiboflapon dose-dependently reduced LTB4, CysLTs, plasma protein extravasation and neutrophil influx induced by peritoneal zymosan injection. Finally, Fiboflapon increases survival time in mice exposed to a lethal intravenous injection of platelet activating factor (PAF)[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C38H43N3O4S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 637.83100 |
| Exact Mass | 637.29700 |
| PSA | 111.77000 |
| LogP | 8.97660 |