444731-52-6
| Name | pazopanib |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
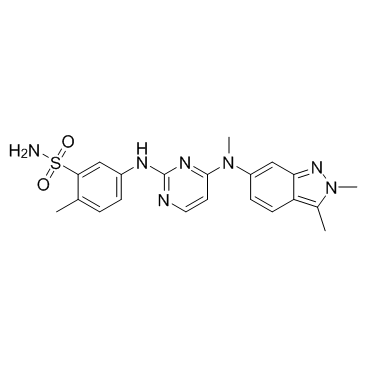
5-({4-[(2,3-Dimethyl-2H-indazol-6-yl)(methyl)amino]-2-pyrimidinyl}amino)-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide
Pazopanib(GW786034) Benzenesulfonamide, 5-[[4-[(2,3-dimethyl-2H-indazol-6-yl)methylamino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-2-methyl- 5-({4-[(2,3-Dimethyl-2H-indazol-6-yl)(methyl)amino]pyrimidin-2-yl}amino)-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide Pazopanib |
| Description | Pazopanib (GW786034) is a novel multi-target inhibitor of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFRβ, c-Kit, FGFR1, and c-Fms with IC50s of 10, 30, 47, 84, 74, 140 and 146 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGFR1:10 nM (IC50) VEGFR2:30 nM (IC50) VEGFR3:47 nM (IC50) PDGFRβ:84 nM (IC50) FGFR1:140 nM (IC50) c-Kit:74 nM (IC50) c-Fms:146 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Pazopanib shows good potency against all the human VEGFR receptors with an IC50 of 10, 30, and 47 nM for VEGFR-1, -2, and -3, respectively. Significant activity is also seen against the closely related tyrosine receptor kinases PDGFRβ, c-Kit, FGF-R1, and c-fms with IC50s of 84, 74, 140, and 146 nM, respectively. In cellular assays, in addition to inhibiting the VEGF-induced proliferation of HUVECs, Pazopanib potently inhibits VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 in HUVEC cells with an IC50 of ~8 nM. Pazopanib possesses good pharmacokinetics in rat, dog, and monkey with low clearances (1.4-1.7 mL/min/kg) and good oral bioavailabilities (72, 47, 65%) dosed at 10, 1, and 5 mg/kg, respectively. The cytochrome P450 profile is also improved with inhibition >10 μM against the isozymes tested, with the exception of 2C9 (7.9 μM)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Treatment of mice with 100 mg/kg of Pazopanib twice daily for five days results in significant inhibition in the degree of vascularization. The antiangiogenic activity of Pazopanib is examined in mice bearing established human xenografts (200−250 mm3) using HT29 (colon carcinoma), A375P (melanoma), and HN5 (head and neck carcinoma) tumors following a standard three-week course of therapy. The HN5 and HT29 xenografts responded better at all doses compared to the A375P model, which is historically more resistant to VEGFR-2 inhibitors. As support that the observed inhibition of xenograft growth is working through an antiangiogenic rather than antitumor mechanism, no antiproliferative activity is observed below 10 μM for Pazopanib against these human tumor lines (HT29, HN5, A375P) growing in serum-containing media. No significant effect on the body weight of mice is observed, and the animals appeared healthy and active throughout the study duration[1]. The quantity of adherent leukocytes in the Pazopanib eye drops group is less than untreated diabetic animals and more than the healthy animals. Average leukocytes adhered to the retinal vasculature in healthy animals is 37.2±7.8, whereas diabetic animals have an average value of 102±15.6, approximately 3-fold higher than healthy animals. Animals treated with 0.5 % w/v Pazopanib suspension demonstrate 69.5±9.5 leukocytes adhered in their retinal vasculature, which is found to be significantly lower than diabetic animals[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | VEGFR enzyme assays for VEGGR1, VEGFR2, and VEGFR3 are run in homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) format in 384-well microtiter plates using a purified, baculovirus-expressed glutathione-S-transferase (GST) fusion protein encoding the catalytic c-terminus of human VEGFR receptor kinases 1, 2, or 3. Reactions are initiated by the addition of 10 μL of activated VEGFR2 kinase solution [final concentration, 1 nM enzyme in 0.1 M 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), pH 7.5, containing 0.1 mg/mL bovine serum albumin (BSA), 300 μM dithiothreitol (DTT)] to 10 μL substrate solution [final concentration, 360 nM peptide, (biotin-aminohexyl-EEEEYFELVAKKKK-NH2), 75 μM ATP, 10 μM MgCl2], and 1 μL of titrated compound in DMSO. Plates are incubated at room temperature for 60 min, and then the reaction is quenched by the addition of 20 μL of 100 mM ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA). After quenching, 20 μL HTRF reagents (final concentration, 15 nM Streptavidin-linked allophycocyanin, 1 nM Europium-labeled antiphosphotyrosine antibody diluted in 0.1 mg/mL BSA, 0.1 M HEPES, pH 7.5) is added and the plates incubated for a minimum of 10 min. The fluorescence at 665 nM is measured with a Wallac Victor plate reader using a time delay of 50 μs[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The effect of Pazopanib on cell proliferation is measured using 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation method using commercially available kits. HUVEC is seeded in medium containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) in type 1 collagen coated 96-well plates and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The medium is aspirated from the cells, and various concentrations of Pazopanib in serum-free medium are added to each well. After 30 min, either VEGF (10 ng/mL) or bFGF (0.3 ng/mL) is added to the wells. Cells are incubated for an additional 72 h and BrdU (10 μM) is added during the last 18 to 24 h of incubation. At the end of incubation, BrdU incorporation in cells is measured by ELISA. Data are fitted with a curve described by the equation, y=Vmax(1−(x/(K+x))), where K is equal to the IC50[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Tumors are initiated by injection of tumor cell suspension in 8−12 week old nude mice. When tumors reach a volume of 100−200 mm3, mice are randomized and divided into groups of eight. Pazopanib is administered once or twice daily at 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg. Animals are euthanized by inhalation of CO2 at the completion of the study. Tumor volume is measured twice weekly by calipers, using the equation: tumor volume (mm3)=(length×width2)/2. Results are routinely reported as % inhibition=1−(average growth of the drug treated population/average growth of vehicle treated control population). Rats[2] Male Brown-Norway (BN; pigmented) rats weighing 200 to 250 g are acclimatized for at least two days prior to any experimental procedure. After overnight fasting for 12-16 h, an intraperitoneal injection of 30 mg/mL solution of Streptozotocin in 10 mM citrate buffer (pH 4.5) is administered (60 mg/kg body weight) to induce diabetes. After 3-4 h of Streptozotocin injection, animals are put on a regular diet and 24 h after Streptozotocin injection, blood sample (5-10 μL) is collected via tail vein. The blood glucose levels in the animals are determined with a glucose monitor. Animals with blood glucose levels greater than 250 mg/dL are considered diabetic. The animals are divided into three groups. Group 1: Healthy (n=12), Group 2: Diabetic (n=12) and Group 3: Diabetic+Treatment (n=12). Treatment is started immediately after diabetes induction. Both eyes are dosed twice daily for 30 days with 0.5 % w/v Pazopanib suspension (10 μL volume in each eye) and animals in all groups are sacrificed on day 31, 16-17 h after last dose on day 30. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 728.8±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 285-289°C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C21H23N7O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 437.518 |
| Flash Point | 394.6±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 437.163391 |
| PSA | 127.41000 |
| LogP | 1.98 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.702 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Risk Phrases | 43-62/63 |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 36/37/39-28B |