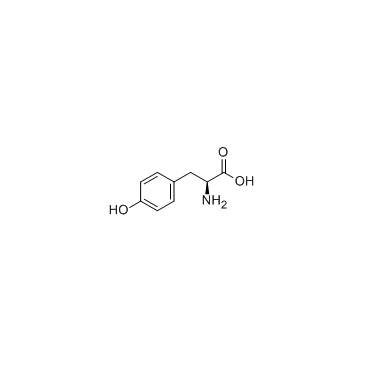
60-18-4
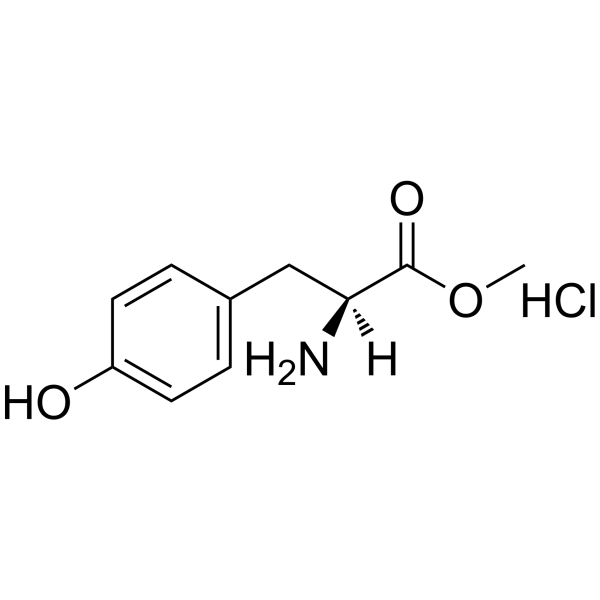
| Name | L-tyrosine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
L-tyrosine zwitterion
hydrogen L-tyrosinate MEVINOLIN LOVALIP a-Amino-p-hydroxyhydrocinnamic Acid L-Phenylalanine, 4-hydroxy- LOVASTIN MEVACOR H-Tyr-OH Tyrosine MFCD00002606 L-Tyr Rovacor Tyr (S)-(-)-Tyrosine Sivlor L-Tyrosine (S)-a-Amino-4-hydroxybenzenepropanoic acid Tyrosine, L- b-(p-Hydroxyphenyl)alanine mevlor Benzenepropanoic acid, α-amino-4-hydroxy-, (S)- Tyrosinum [Latin] (S)-a-amino-4-hydroxy-Benzenepropanoic acid (S)-tyrosine (S)-α-amino-4-hydroxy-Benzenepropanoic acid EINECS 200-460-4 msd803 Paschol |
| Description | L-Tyrosine is a non-essential amino acid which can inhibit citrate synthase activity in the posterior cortex. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Results show that L-Tyrosine in vitro inhibits citrate synthase activity in the posterior cortex (2.0 and 4.0 mM), malate dehydrogenase is not altered by L-Tyrosine and succinate dehydrogenase is increased in the posterior cortex (0.1, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mM), hippocampus (1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mM), striatum (4.0 mM) and liver (0.1, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mM). When complex I activity is analyzed, inhibition is observed in hippocampus (4.0 mM). In addition to inhibition in the hippocampus, complex II also is inhibited in the posterior cortex (0.1, 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mM) and liver (1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mM). For complex II–III, activity is not altered by L-Tyrosine, and complex IV activity has decreased in the posterior cortex (1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mM) following treatment with L-Tyrosine[1]. |
| In Vivo | The acute administration of L-Tyrosine inhibits the activity of citrate synthase in the posterior cortex and liver; however, in the striatum, the activity is increased. The results also demonstrate that acute administration of L-Tyrosine inhibits malate dehydrogenase and complex II, II–III and IV of the mitochondrial respiratory chain activity in the posterior cortex and liver of rats. The succinate dehydrogenase enzyme and complex I activity are inhibited in the posterior cortex and increased in the striatum. Furthermore, energy metabolism in the hippocampus is not amended by an acute administration of L-Tyrosine[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Posterior cortex, hippocampus, striatum and liver supernatants of 30-day-old rats are pre-incubated for 30 min at 30°C in the presence of L-Tyrosine (Tyr) at final concentrations ranging from 0.1, 1.0, 2.0 or 4.0 mM, and the activities of citrate synthase, malate dehydrogenase and respiratory chain complexes I, II, II–III and IV are evaluated[1]. |
| Animal Admin | The equivalent of 500 mg/kg body weight of free L-Tyrosine is intraperitoneally administered in 30-day-old rats. Controls receive in saline solution. About 1 h after injections, rats are killed by decapitation without anesthesia[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 385.2±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 181.189 |
| Flash Point | 186.7±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 181.073898 |
| PSA | 83.55000 |
| LogP | 0.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.614 |
| Water Solubility | 0.45 g/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YP2275600 |
| HS Code | 29225000 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |