51551-29-2
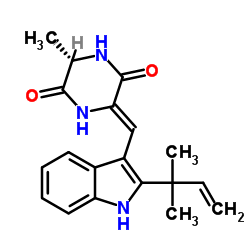
| Name | (3S,6Z)-3-Methyl-6-{[2-(2-methyl-3-buten-2-yl)-1H-indol-3-yl]meth ylene}-2,5-piperazinedione |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2,5-Piperazinedione, 3-[[2-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propen-1-yl)-1H-indol-3-yl]methylene]-6-methyl-, (3Z,6S)-
(3S,6Z)-3-Methyl-6-{[2-(2-methyl-3-buten-2-yl)-1H-indol-3-yl]methylene}-2,5-piperazinedione (3S,6Z)-3-methyl-6-{[2-(2-methylbut-3-en-2-yl)-1H-indol-3-yl]methylidene}piperazine-2,5-dione |
| Description | Neoechinulin A is an isoprenyl indole alkaloid that exhibits scavenging, neurotrophic factor-like, and anti-apoptotic activities. Neoechinulin A induces memory improvements and antidepressant-like effects in mice[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Neoechinulin A (RAW264.7 macrophages; 3 hours; cells then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 18 hours) suppresses PGE2, TNF-α, and IL-1β production in a dose-dependent manner[2]. Neoechinulin A can suppress the production of pro-inflammatory mediators and cytokines including NO, PGE2, TNF-α, and IL-1β. Further, it reduced the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by inhibiting the NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways[2]. Neoechinulin A suppresses amyloid-β oligomer-induced microglia activation and thereby protects PC-12 cells from inflammation-mediated toxicity[3]. |
| In Vivo | In the Y-maze test, the intracerebroventicular (i.c.v.) administration of LPS (10 μg/mouse) significantly decreased spontaneous alternation behavior, which was prevented by the prior administration of neoechinulin A (300ng/mouse, i.c.v.)[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 655.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H21N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 323.389 |
| Flash Point | 350.4±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 323.163391 |
| PSA | 73.99000 |
| LogP | 2.55 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.628 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|