146672-02-8
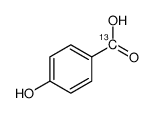
| Name | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid-|A-13C |
| Description | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid-13C is the 13C labeled 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid[1]. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid, could inhibit most gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria, with an IC50 of 160 μg/mL[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 214-215ºC(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 139.11300 |
| Exact Mass | 139.03500 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 1.09040 |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |