Ebselen oxide
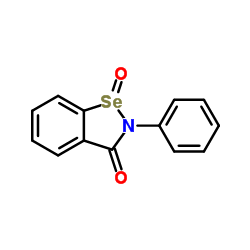
Ebselen oxide structure
|
Common Name | Ebselen oxide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104473-83-8 | Molecular Weight | 290.176 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 277.3±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H9NO2Se | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 121.5±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Ebselen oxideEbselen oxide, the selenone analogue of Ebselen, covalently modifies diguanylate cyclase (DGC) to inhibit c-di-GMP-receptor interactions and reduces DGC activity. Ebselen oxide also inhibits alginate production (IC50=14 μM) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ebselen oxide inhibits HDAC1, HDAC3, HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC6, HDAC7, HDAC8, and HDAC9 (IC50 ranging from 0.2 to 4.7 μM)[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 1-Oxide-2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one Ebselen selenoxide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ebselen oxide, the selenone analogue of Ebselen, covalently modifies diguanylate cyclase (DGC) to inhibit c-di-GMP-receptor interactions and reduces DGC activity. Ebselen oxide also inhibits alginate production (IC50=14 μM) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ebselen oxide inhibits HDAC1, HDAC3, HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC6, HDAC7, HDAC8, and HDAC9 (IC50 ranging from 0.2 to 4.7 μM)[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Ebselen oxide, is a covalent inhibitor of c-di-GMP allosteric binding to I-site containing proteins, diguanylate cyclase (DGC) activity[1]. Ebselen oxide inhibits diguanylate cyclase from synthesizing c-di-GMP. Ebselen oxide exhibits increased potency on HDAC8 (IC50=0.2 μM) in comparison with Ebselen[3]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 277.3±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H9NO2Se |
| Molecular Weight | 290.176 |
| Flash Point | 121.5±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 290.979858 |
| PSA | 37.38000 |
| LogP | 1.53770 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H331-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P301 + P310-P311-P501 |
| RIDADR | UN 3283 6.1 / PGII |
|
~77% 
Ebselen oxide CAS#:104473-83-8 |
| Literature: Mlochowski, Jacek; Kloc, Krystian; Syper, Ludwik; Inglot, Anna D.; Piasecki, Egbert Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1993 , # 12 p. 1239 - 1244 |
|
~71% 
Ebselen oxide CAS#:104473-83-8 |
| Literature: Fisher, Hartmut; Dereu, Norbert Bulletin des Societes Chimiques Belges, 1987 , vol. 96, # 10 p. 757 - 768 |
|
~% 
Ebselen oxide CAS#:104473-83-8 |
| Literature: Daiber, Andreas; Zou, Ming-Hui; Bachschmid, Markus; Ullrich, Volker Biochemical Pharmacology, 2000 , vol. 59, # 2 p. 153 - 160 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
|
AMACR amplification in myxofibrosarcomas: a mechanism of overexpression that promotes cell proliferation with therapeutic relevance.
Clin. Cancer Res. 20(23) , 6141-52, (2014) Myxofibrosarcomas frequently display arm-level gains on 5p. We characterized the pathogenetic and therapeutic relevance of the α-methylacyl coenzyme A racemase (AMACR) at 5p13.3.AMACR mRNA expression ... |
|
|
AMACR amplification and overexpression in primary imatinib-naïve gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a driver of cell proliferation indicating adverse prognosis.
Oncotarget 5(22) , 11588-603, (2014) Non-random gains of chromosome 5p have been observed in clinically aggressive gastrointestinal stromal tumors, whereas the driving oncogenes on 5p remain to be characterized. We used an integrative ge... |
| 2-Phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3(2H)-one 1-oxide |
| 1,2-Benzisoselenazole-1,3-dione, 2-phenyl |
| 1-oxo-2-phenyl-1λ<sup>4</sup>,2-benzoselenazol-3-one |
| 1,2-Benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one, 2-phenyl-, 1-oxide |

 CAS#:150-60-7
CAS#:150-60-7 CAS#:10496-16-9
CAS#:10496-16-9 CAS#:2550-40-5
CAS#:2550-40-5 CAS#:118398-40-6
CAS#:118398-40-6 CAS#:80028-57-5
CAS#:80028-57-5