Proinsulin C-Peptide (55-89) human
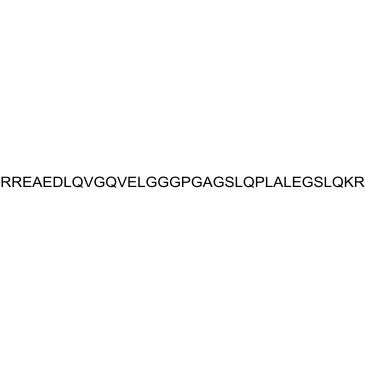
Proinsulin C-Peptide (55-89) human structure
|
Common Name | Proinsulin C-Peptide (55-89) human | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 11097-48-6 | Molecular Weight | 3616.99000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C153H259N49O52 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Proinsulin C-Peptide (55-89) humanProinsulin C-Peptide (55-89), human is a peptide fragment of the cleavage product of proinsulin[1]. |
| Name | Proinsulin connecting peptide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Proinsulin C-Peptide (55-89), human is a peptide fragment of the cleavage product of proinsulin[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C153H259N49O52 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 3616.99000 |
| Exact Mass | 3614.91000 |
| PSA | 1646.18000 |
| LogP | 0.02050 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Molecular and cellular effects of C-peptide--new perspectives on an old peptide.
Exp. Diabesity Res. 5 , 15-23, (2004) New results present C-peptide as a biologically active peptide hormone in its own right. Although C-peptide is formed from proinsulin and cosecreted with insulin, it is a separate entity with biochemi... |
|
|
Cellular mechanisms by which proinsulin C-peptide prevents insulin-induced neointima formation in human saphenous vein.
Diabetologia 53 , 1761-71 , (2010) Endothelial cells (ECs) and smooth muscle cells (SMCs) play key roles in the development of intimal hyperplasia in saphenous vein (SV) bypass grafts. In diabetic patients, insulin administration contr... |
|
|
Studies on human proinsulin. Isolation and amino acid sequence of the human pancreatic C-peptide.
J. Biol. Chem. 246 , 1375, (1971)
|
| Insulin C chain |
| C-Peptide human |
| Proinsulin C-Peptide (55-89) human |
| C-PEPTIDE (1-35),HUMAN |
| Proinsulin (31-65), human |