Vanillic acid
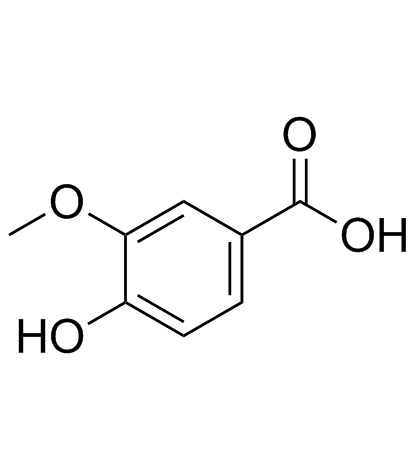
Vanillic acid structure
|
Common Name | Vanillic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 121-34-6 | Molecular Weight | 168.147 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 353.4±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O4 | Melting Point | 208-210 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 149.4±17.2 °C | |
Use of Vanillic acidVanillic acid is a flavoring agent found in edible plants and fruits. Vanillic acid inhibits NF-κB activation. Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and chemopreventive effects[1]. |
| Name | vanillic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Vanillic acid is a flavoring agent found in edible plants and fruits. Vanillic acid inhibits NF-κB activation. Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and chemopreventive effects[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p65 |
| In Vitro | Vanillic acid inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced phosphorylation of IκB (cytoplasmatic NF-κB inhibitor) in the cytoplasm extract and NF-κB p65 subunit expression in the nuclear extract of macrophages in vitro as determined by Western blot[1]. Vanillic acid treatment reverses the Aβ1-42-induced elevated expression of IKK-β/NF-κB and reduces the activity of IKKβ/NF-κB. Vanillic acid is non-toxic to HT22 cells at all three concentrations (50, 100 and 200 μM); Vanillic acid co-treatment with Aβ1-42 significantly increases (1.5-, 1.9- and 2-fold respectively) cell viability. Aβ1-42 (5 μM) treatment results in a significant increase (1.6-fold) in ROS levels compared with the control cells. In contrast, Vanillic acid treatment at all three different concentrations (50, 100 and 200 μM) reduces (1.1-, 1.3- and 1.4-fold respectively) ROS levels, indicating that Vanillic acid is a potent antioxidant[2]. |
| In Vivo | Vanillic acid (30 mg/kg, ip, 1 h) inhibits Carrageenan-induced NF-κB activation. Mice receive Vanillic acid (30 mg/kg, ip) 1 h before ipl injection of Carrageenan (300 μg/paw), and samples of the cutaneous plantar tissues are collected 3 h after stimulus injection. Carrageenan-induced activation of NF-κB is observed by a decrease in the ratio of total NF-κB/p-NF-κB, while treatment with Vanillic acid as well as the control drug Indomethacin (5 mg/kg, ip, diluted in Tris/HCl buffer, 40 min before stimulus) inhibits Carrageenan-induced activation of NF-κB[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The viability of HT22 cells is assessed with the MTT assay. Cells are cultured in 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 104 cells per well in 100 μL of Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM). After 24 h, the medium is replaced with fresh medium containing Aβ1-42 (5 μM), with three different concentrations (50, 100 and 200 μM) of Vanillic acid either alone or in combination with Aβ1-42 (5 μM), and the cells are incubated for an additional 24 h. The control cells receive only DMEM. Following this, the cells are incubated with MTT solution for another 2-4 h at 37°C. Subsequently, the medium in each well is replaced with DMSO. Finally, the absorbance of the solution in each well at 570 nm is measured using an ApoTox instrument. All experiments are performed independently in triplicate[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] During the experiments, Male Swiss mice (25-30 g) receive intraperitoneal (3, 10, or 30 mg/kg) treatment with Vanillic acid or vehicle (5% Tween 80 diluted in saline) 1 h before or 24 h after inflammatory stimuli injection[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 353.4±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 208-210 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 168.147 |
| Flash Point | 149.4±17.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 168.042252 |
| PSA | 66.76000 |
| LogP | 1.33 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.586 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | YW5300000 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Antimicrobial activity of natural products from the flora of Northern Ontario, Canada.
Pharm. Biol. 53(6) , 800-6, (2015) The number of multidrug resistant (MDR) microorganisms is increasing and the antimicrobial resistance expressed by these pathogens is generating a rising global health crisis. In fact, there are only ... |
|
|
Comparison between ATR-IR, Raman, concatenated ATR-IR and Raman spectroscopy for the determination of total antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content of Chinese rice wine.
Food Chem. 194 , 671-9, (2015) The application of attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy (ATR-IR), Raman spectroscopy (RS) and combination of ATR-IR and RS for measurements of total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and total ... |
|
|
Antagonistic control of a dual-input mammalian gene switch by food additives.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(14) , e116, (2014) Synthetic biology has significantly advanced the design of mammalian trigger-inducible transgene-control devices that are able to programme complex cellular behaviour. Fruit-based benzoate derivatives... |
| 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid |
| EINECS 204-466-8 |
| 4-hydroxy-m-Anisic acid |
| Benzoic acid, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy- |
| 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzoic acid |
| Vanillic acid |
| MFCD00002551 |
| Acid, Vanillic |
 CAS#:121-33-5
CAS#:121-33-5 CAS#:2426-87-1
CAS#:2426-87-1 CAS#:93-51-6
CAS#:93-51-6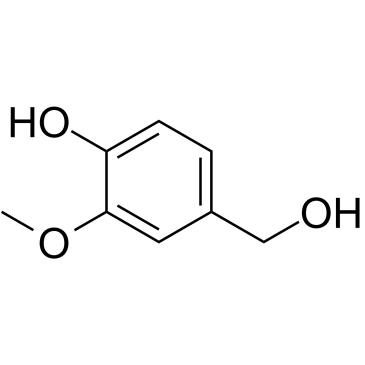 CAS#:498-00-0
CAS#:498-00-0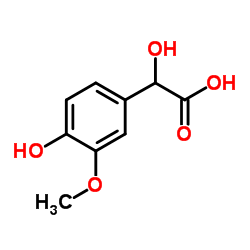 CAS#:55-10-7
CAS#:55-10-7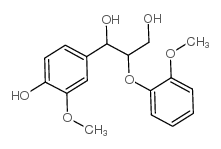 CAS#:7382-59-4
CAS#:7382-59-4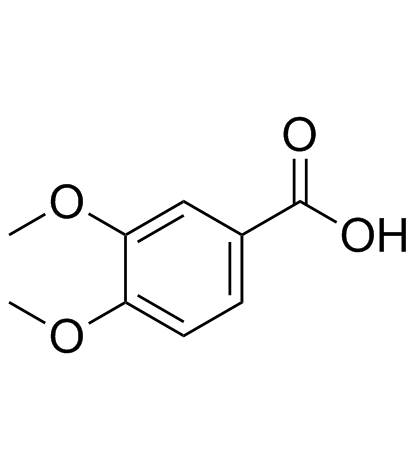 CAS#:93-07-2
CAS#:93-07-2 CAS#:1486-53-9
CAS#:1486-53-9 CAS#:4421-08-3
CAS#:4421-08-3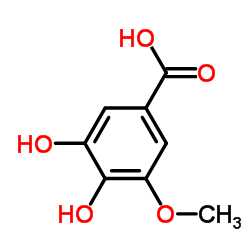 CAS#:3934-84-7
CAS#:3934-84-7 CAS#:3251-56-7
CAS#:3251-56-7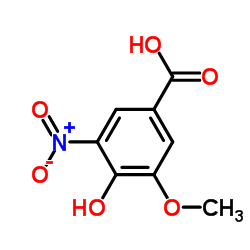 CAS#:15785-54-3
CAS#:15785-54-3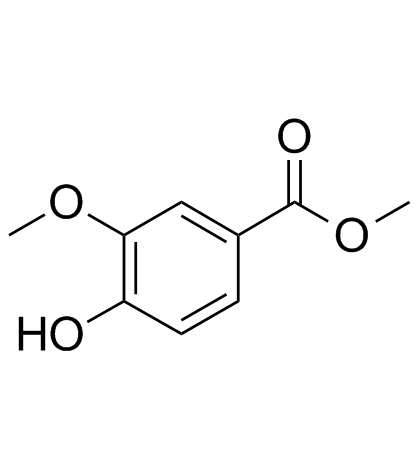 CAS#:3943-74-6
CAS#:3943-74-6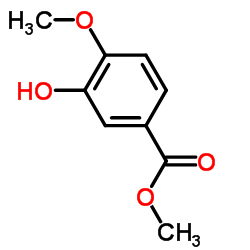 CAS#:6702-50-7
CAS#:6702-50-7 CAS#:140658-45-3
CAS#:140658-45-3![4-[5-(4-carboxy-2-methoxy-5-nitrophenoxy)pentoxy]-5-methoxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/228/145325-48-0.png) CAS#:145325-48-0
CAS#:145325-48-0 CAS#:91203-74-6
CAS#:91203-74-6 CAS#:19072-58-3
CAS#:19072-58-3
