Ammonium Chloride

Ammonium Chloride structure
|
Common Name | Ammonium Chloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 12125-02-9 | Molecular Weight | 53.49150 | |
| Density | 1.52 | Boiling Point | 100 °C750 mm Hg | |
| Molecular Formula | ClH4N | Melting Point | 340 °C (subl.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Ammonium ChlorideAmmonium chloride, as a heteropolar compound with pH value regulation, can cause intracellular alkalization and metabolic acidosis thus effecting enzymatic activity and influencing the process of biological system. Ammonium chloride is an autophagy inhibitor[1][2]. |
| Name | ammonium chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ammonium chloride, as a heteropolar compound with pH value regulation, can cause intracellular alkalization and metabolic acidosis thus effecting enzymatic activity and influencing the process of biological system. Ammonium chloride is an autophagy inhibitor[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), a lysosomotropic agent that raises intralysosomal pH, reduces the yield of reovirus during infection of mouse L cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Ammonium chloride (0.28 M in drinking water) promotes the survival of myocardial cells in vivo by decreasing contractile dysfunction, cardiac hypertrophy, inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy[1]. Animal Model: 8-9-week-old C57B/L6 mice[1] Dosage: 0.28 M in drinking water (5 mg/kg doxorubicin once a week for 2 weeks) Administration: 0.28 M in drinking water (5 mg/kg doxorubicin once a week for 2 weeks) Result: Effectively improved doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction in mice. |
| References |
| Density | 1.52 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 100 °C750 mm Hg |
| Melting Point | 340 °C (subl.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | ClH4N |
| Molecular Weight | 53.49150 |
| Exact Mass | 53.00320 |
| LogP | 1.17820 |
| Vapour density | 1.9 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 160.4 °C) |
| Index of Refraction | 1.642 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases. |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36-S26 |
| RIDADR | UN 9085 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | BP4550000 |
| HS Code | 2827101000 |
|
~0% 
Ammonium Chloride CAS#:12125-02-9 |
| Literature: AGRA GROUP, A.S.; KYSILKA, Vladimir; KOPENEC, Jiri; KREPELKA, Jiri Patent: WO2010/45895 A2, 2010 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 11 ; |
|
~% 
Ammonium Chloride CAS#:12125-02-9 |
| Literature: EP1731510 A1, ; Page/Page column 5 ; |
|
~% 
Ammonium Chloride CAS#:12125-02-9 |
| Literature: EP1058547 B1, ; Page/Page column 5 ; |
|
~% 
Ammonium Chloride CAS#:12125-02-9 |
| Literature: WO2008/94664 A1, ; Page/Page column 25 ; |
|
~% 
Ammonium Chloride CAS#:12125-02-9 |
| Literature: Angewandte Chemie - International Edition, , vol. 51, # 47 p. 11731 - 11735 Angew. Chem., , vol. 124, # 47 p. 11901 - 11905,5 |
|
~% 
Ammonium Chloride CAS#:12125-02-9 |
| Literature: Electrochimica Acta, , vol. 56, # 1 p. 215 - 221 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
| HS Code | 2827101000 |
|---|
|
Improved ethanol tolerance and ethanol production from glycerol in a streptomycin-resistant Klebsiella variicola mutant obtained by ribosome engineering.
Bioresour. Technol. 176 , 156-62, (2014) To improve the ethanol tolerance of the Klebsiella variicola strain TB-83, we obtained the streptomycin-resistant, ethanol-tolerant mutant strain TB-83D by a ribosome engineering approach. Strain TB-8... |
|
|
A synthetic O2 -tolerant butanol pathway exploiting native fatty acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112(1) , 120-8, (2014) Several synthetic metabolic pathways for butanol synthesis have been reported in Escherichia coli by modification of the native CoA-dependent pathway from selected Clostridium species. These pathways ... |
|
|
Systematic comparison of the effects of alpha-synuclein mutations on its oligomerization and aggregation.
PLoS Genet. 10(11) , e1004741, (2014) Aggregation of alpha-synuclein (ASYN) in Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites is the typical pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease (PD) and other synucleinopathies. Furthermore, mutations in the gene ... |
| Ammonium chloride |
| ammonia chloride |
| amine hydrochloride |
| Ammonium Chlorid |
| threo-amine hydrochloride |
| EINECS 235-186-4 |
| ammonium cloride |
| MFCD00011420 |
![2-[[2-Ethyl-1-(phenylmethyl)-1H-indol-4-yl]oxy]acetic acid methyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/310/172733-07-2.png)

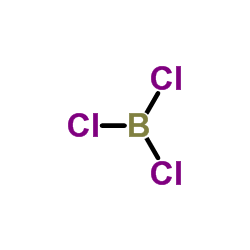

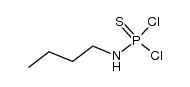
 CAS#:940-71-6
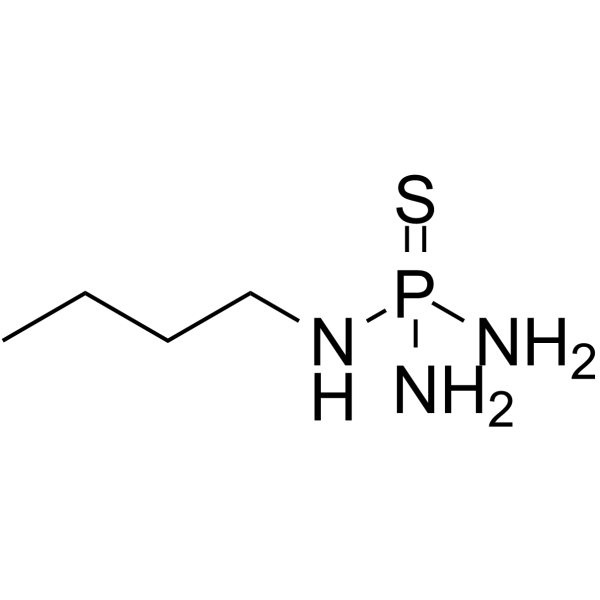
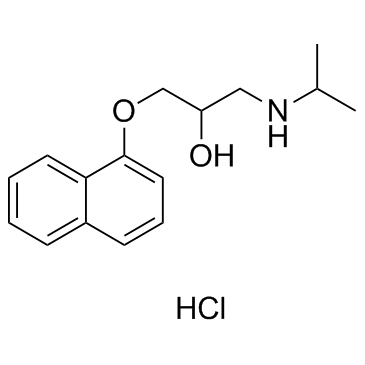
CAS#:940-71-6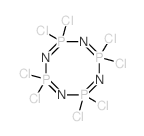 CAS#:2950-45-0
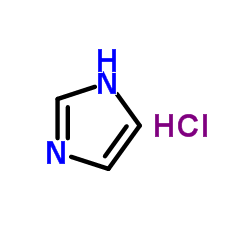
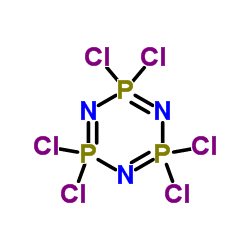
CAS#:2950-45-0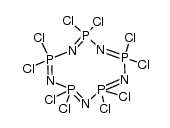 CAS#:13596-41-3
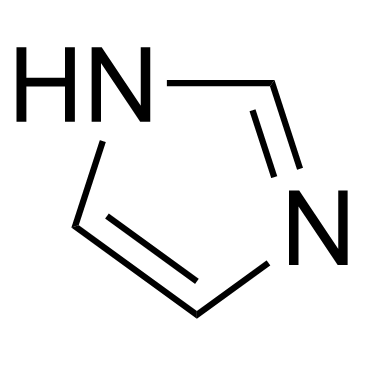
CAS#:13596-41-3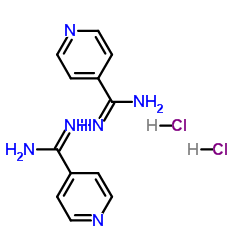 CAS#:6345-27-3
CAS#:6345-27-3![2-bromo-5-[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxybenzaldehyde structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/274/351418-50-3.png) CAS#:351418-50-3
CAS#:351418-50-3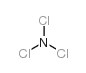 CAS#:10025-85-1
CAS#:10025-85-1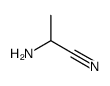 CAS#:51806-98-5
CAS#:51806-98-5
